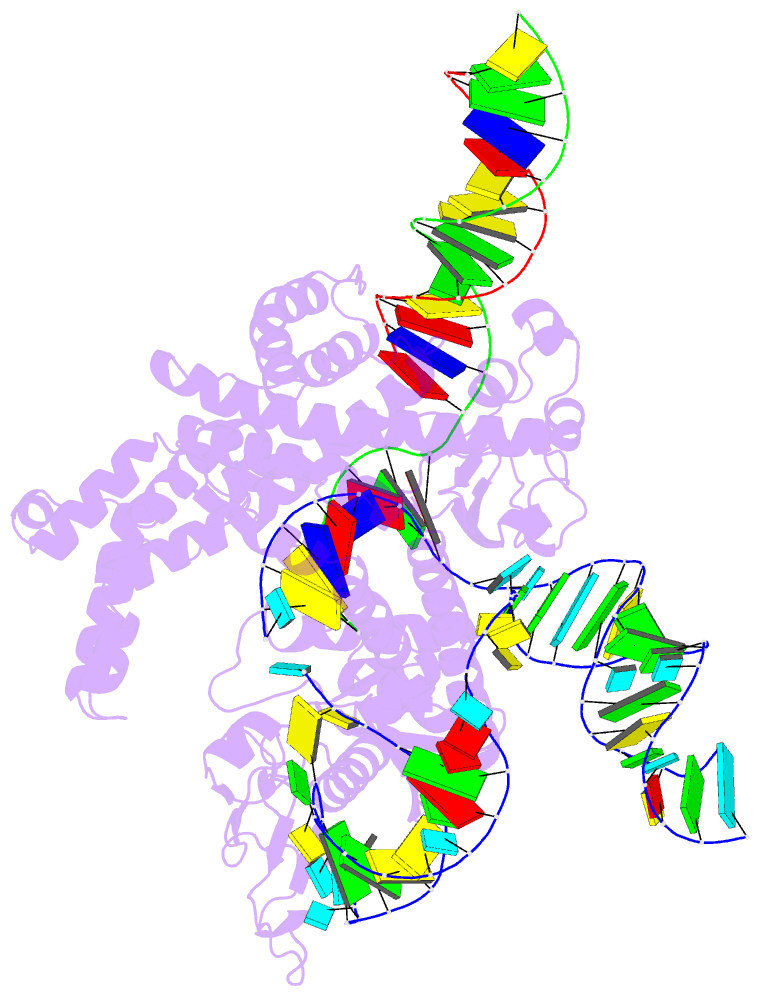
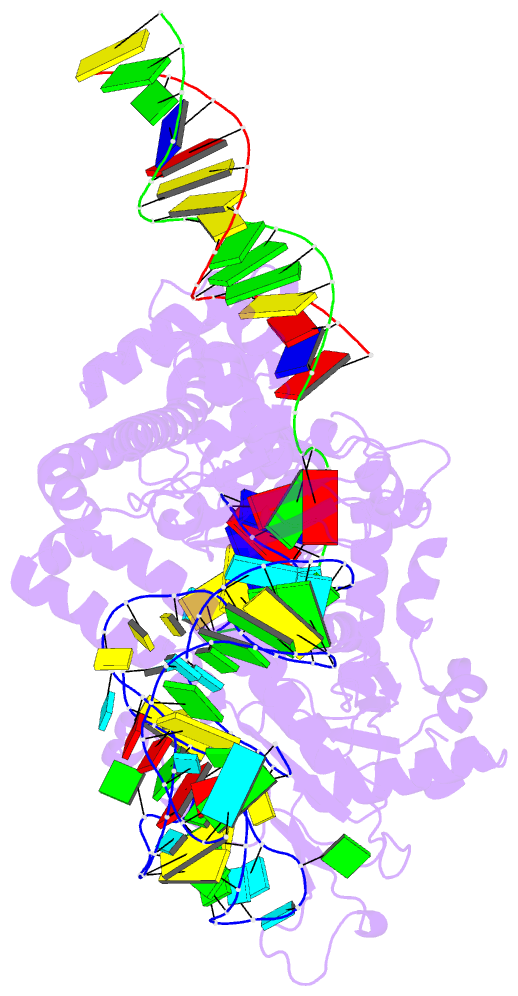
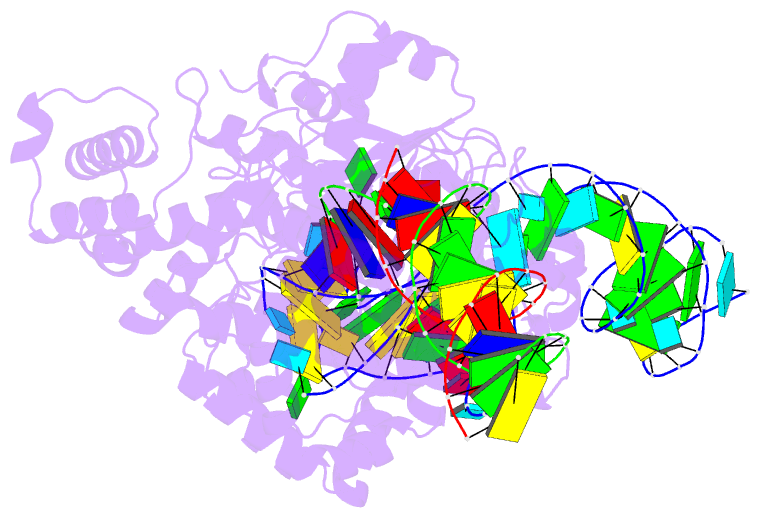
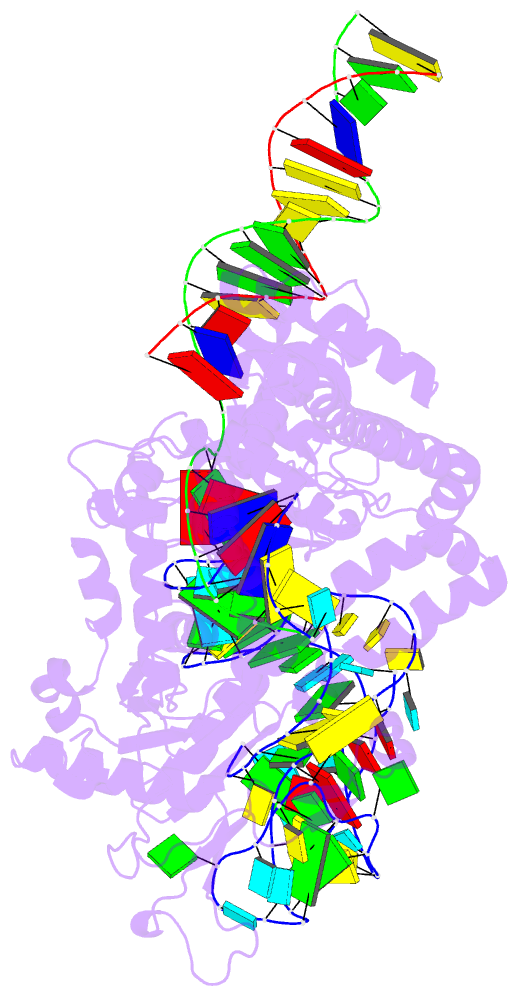
Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
-
9ceu;
SNAP-derived features in text and
JSON formats
- Class
- RNA binding protein-RNA-DNA
- Method
- cryo-EM (3.29 Å)
- Summary
- Spizellomyces punctatus fanzor (spufz) state 1
- Reference
-
Xu P, Saito M, Faure G, Maguire S, Chau-Duy-Tam Vo S,
Wilkinson ME, Kuang H, Wang B, Rice WJ, Macrae RK, Zhang
F (2024): "Structural
insights into the diversity and DNA cleavage mechanism of
Fanzor." Cell, 187,
5238-5252.e20. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2024.07.050.
- Abstract
- Fanzor (Fz) is an ωRNA-guided endonuclease extensively
found throughout the eukaryotic domain with unique gene
editing potential. Here, we describe the structures of Fzs
from three different organisms. We find that Fzs share a
common ωRNA interaction interface, regardless of the length
of the ωRNA, which varies considerably across species. The
analysis also reveals Fz's mode of DNA recognition and
unwinding capabilities as well as the presence of a
non-canonical catalytic site. The structures demonstrate
how protein conformations of Fz shift to allow the binding
of double-stranded DNA to the active site within the
R-loop. Mechanistically, examination of structures in
different states shows that the conformation of the lid
loop on the RuvC domain is controlled by the formation of
the guide/DNA heteroduplex, regulating the activation of
nuclease and DNA double-stranded displacement at the single
cleavage site. Our findings clarify the mechanism of Fz,
establishing a foundation for engineering efforts.