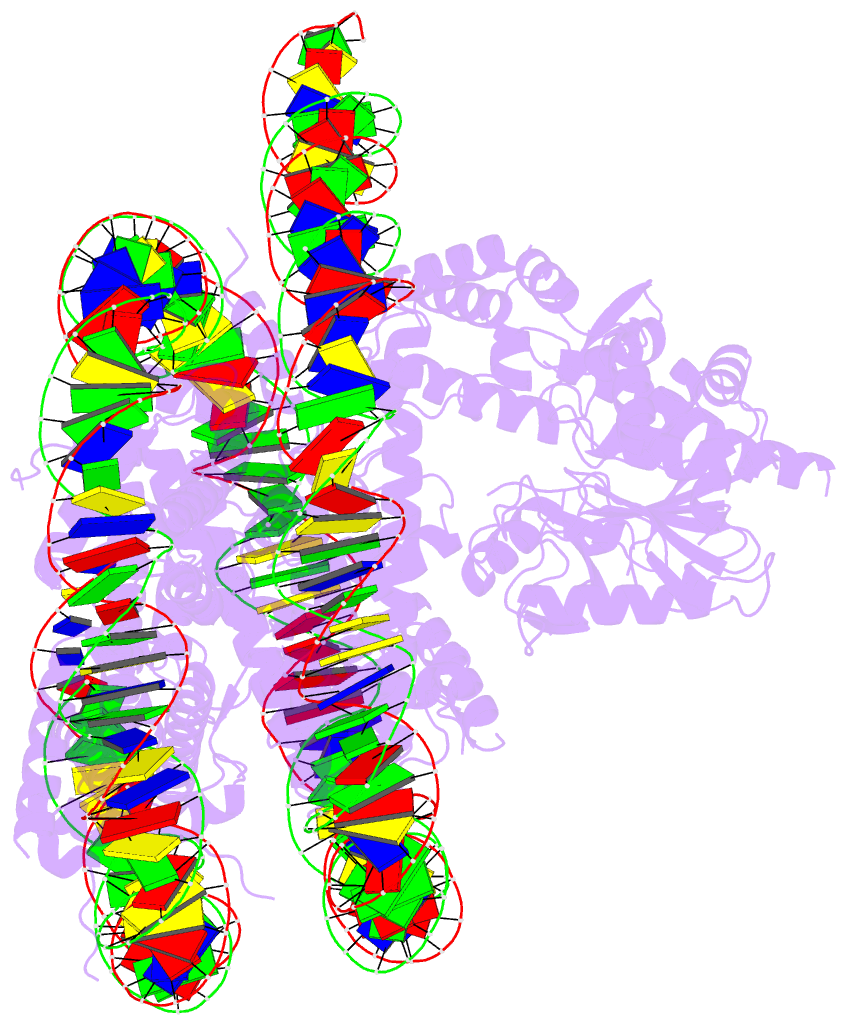
Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
-
8svf;
SNAP-derived features in text and
JSON formats
- Class
- nuclear protein-DNA-RNA
- Method
- cryo-EM (3.2 Å)
- Summary
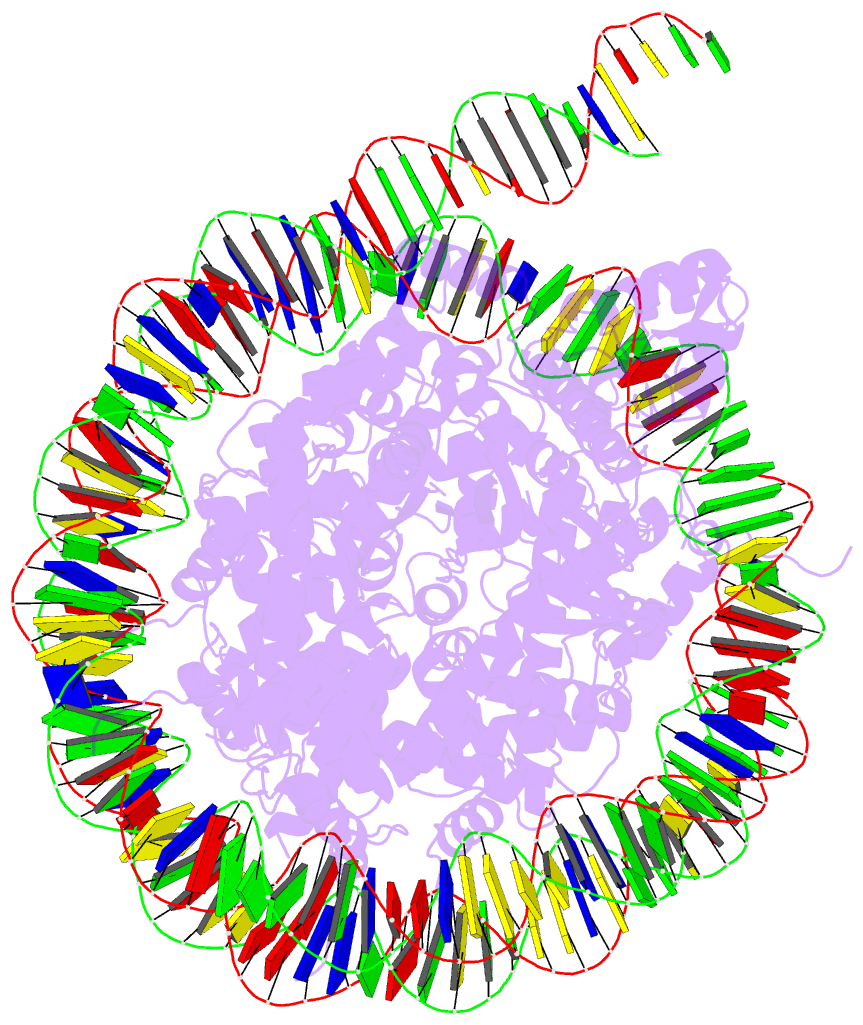
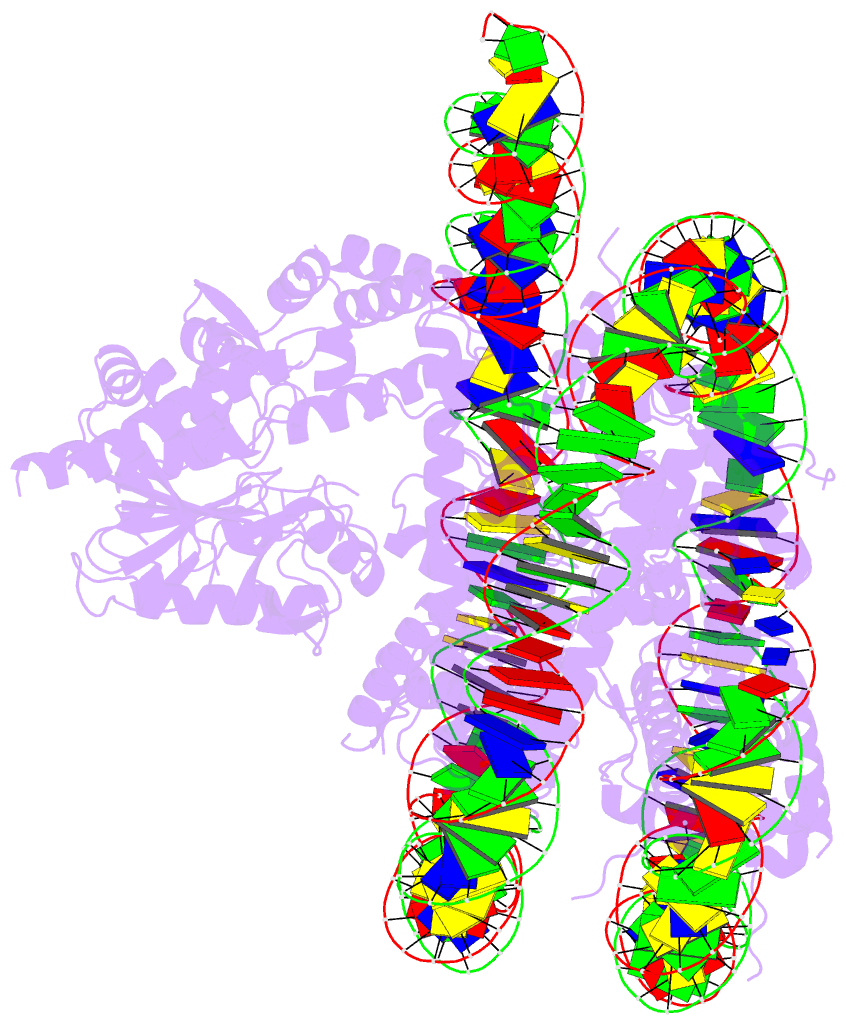
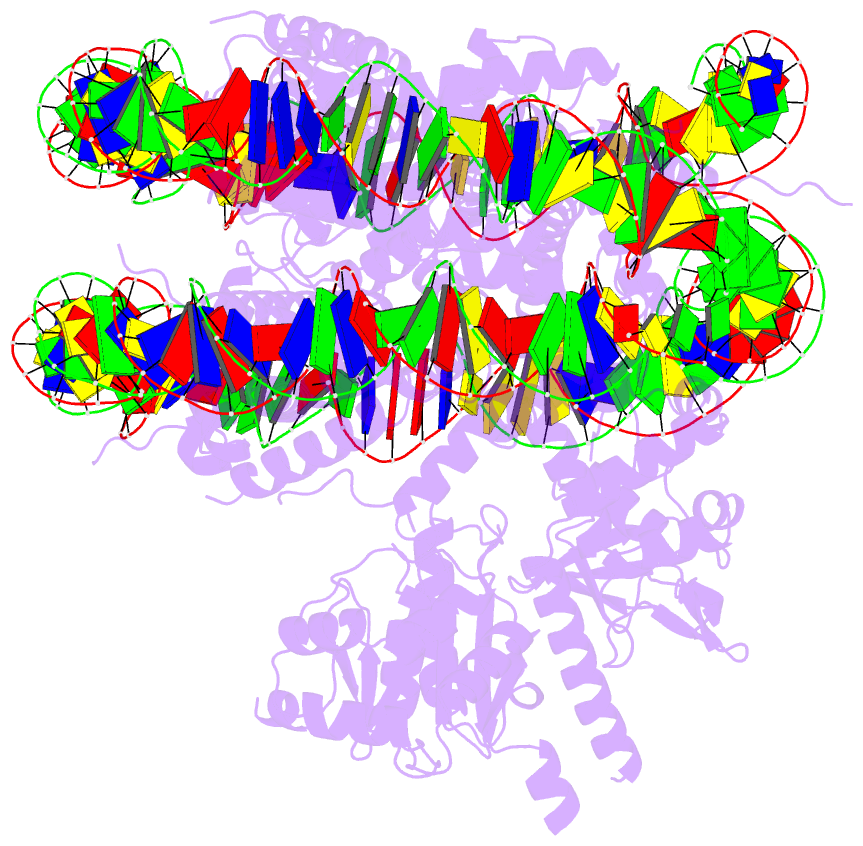
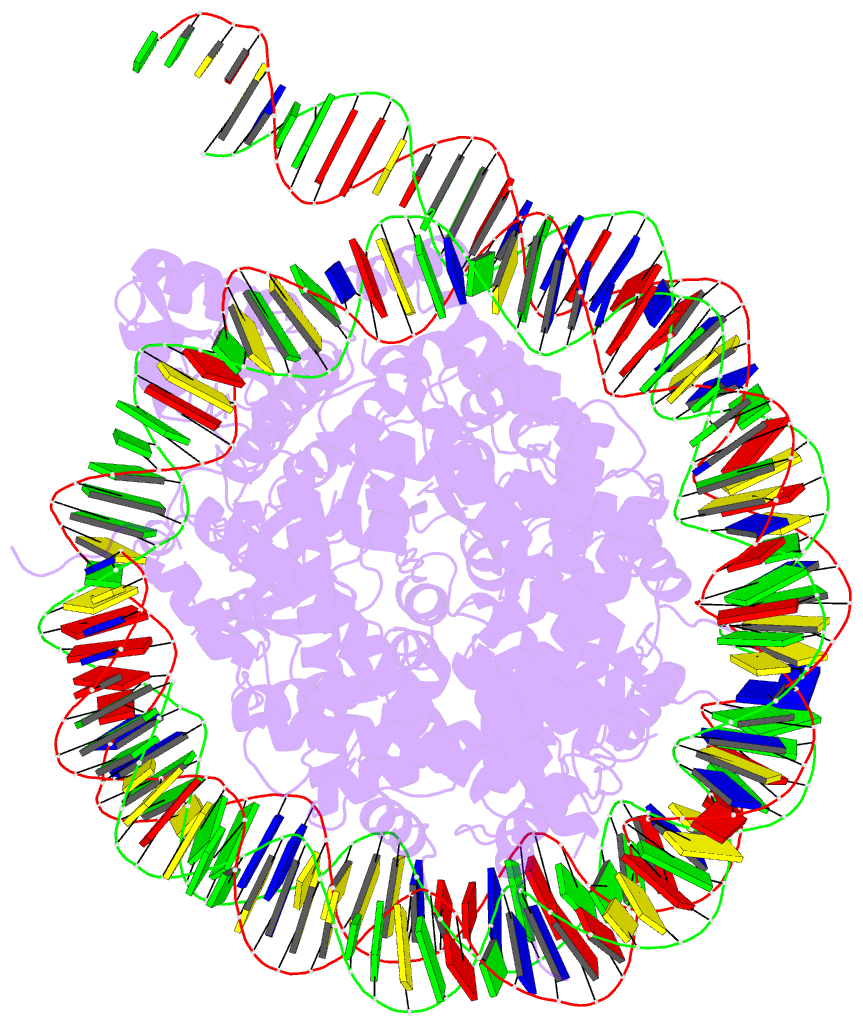
- Bap1-asxl1 bound to the h2ak119ub nucleosome
- Reference
-
Thomas JF, Valencia-Sanchez MI, Tamburri S, Gloor SL,
Rustichelli S, Godinez-Lopez V, De Ioannes P, Lee R,
Abini-Agbomson S, Gretarsson K, Burg JM, Hickman AR, Sun
L, Gopinath S, Taylor HF, Sun ZW, Ezell RJ, Vaidya A,
Meiners MJ, Cheek MA, Rice WJ, Svetlov V, Nudler E, Lu C,
Keogh MC, Pasini D, Armache KJ (2023): "Structural
basis of histone H2A lysine 119 deubiquitination by
Polycomb repressive deubiquitinase BAP1/ASXL1."
Sci Adv, 9, eadg9832. doi:
10.1126/sciadv.adg9832.
- Abstract
- Histone H2A lysine 119 (H2AK119Ub) is monoubiquitinated
by Polycomb repressive complex 1 and deubiquitinated by
Polycomb repressive deubiquitinase complex (PR-DUB). PR-DUB
cleaves H2AK119Ub to restrict focal H2AK119Ub at Polycomb
target sites and to protect active genes from aberrant
silencing. The PR-DUB subunits (BAP1 and ASXL1) are among
the most frequently mutated epigenetic factors in human
cancers. How PR-DUB establishes specificity for H2AK119Ub
over other nucleosomal ubiquitination sites and how
disease-associated mutations of the enzyme affect activity
are unclear. Here, we determine a cryo-EM structure of
human BAP1 and the ASXL1 DEUBAD in complex with a H2AK119Ub
nucleosome. Our structural, biochemical, and cellular data
reveal the molecular interactions of BAP1 and ASXL1 with
histones and DNA that are critical for restructuring the
nucleosome and thus establishing specificity for H2AK119Ub.
These results further provide a molecular explanation for
how >50 mutations in BAP1 and ASXL1 found in cancer can
dysregulate H2AK119Ub deubiquitination, providing insight
into understanding cancer etiology.