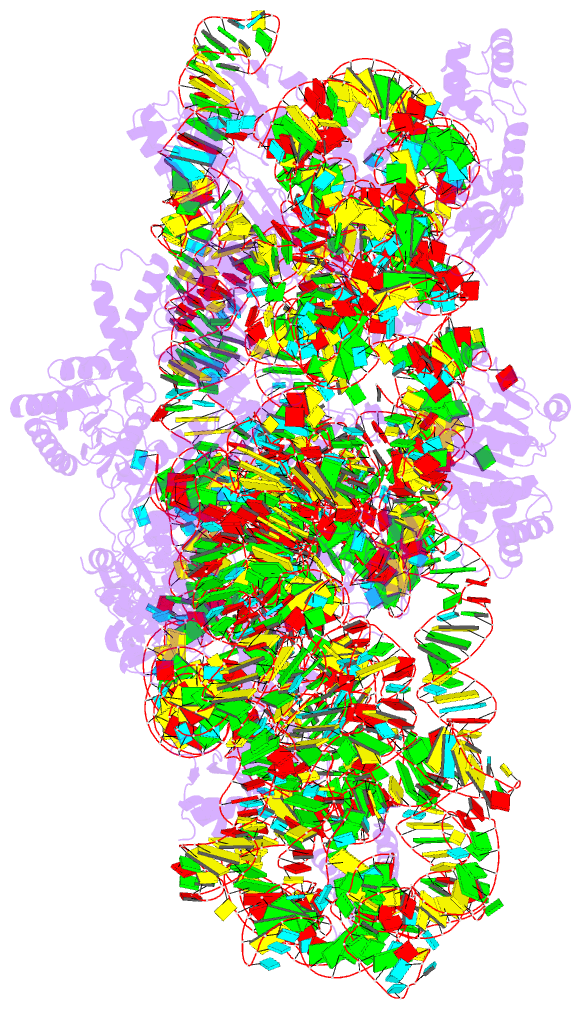
Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
-
7v2o;
SNAP-derived features in text and
JSON formats
- Class
- ribosome
- Method
- cryo-EM (3.5 Å)
- Summary
- T.thermophilus 30s ribosome with ksga, class k4
- Reference
-
Singh J, Raina R, Vinothkumar KR, Anand R (2022):
"Decoding
the Mechanism of Specific RNA Targeting by Ribosomal
Methyltransferases." Acs Chem.Biol.,
17, 829-839. doi: 10.1021/acschembio.1c00732.
- Abstract
- Methylation of specific nucleotides is integral for
ribosomal biogenesis and also serves as a common mechanism
to confer antibiotic resistance by pathogenic bacteria.
Here, by determining the high-resolution structure of the
30S-KsgA complex by cryo-electron microscopy, a state was
captured, where KsgA juxtaposes between helices h44 and h45
of the 30S ribosome, separating them, thereby enabling
remodeling of the surrounded rRNA and allowing the cognate
site to enter the methylation pocket. With the structure as
a guide, several mutant versions of the ribosomes, where
interacting bases in the catalytic helix h45 and
surrounding helices h44, h24, and h27, were mutated and
evaluated for their methylation efficiency revealing
factors that direct the enzyme to its cognate site with
high fidelity. The biochemical studies show that the
three-dimensional environment of the ribosome enables the
interaction of select loop regions in KsgA with the
ribosome helices paramount to maintain selectivity.