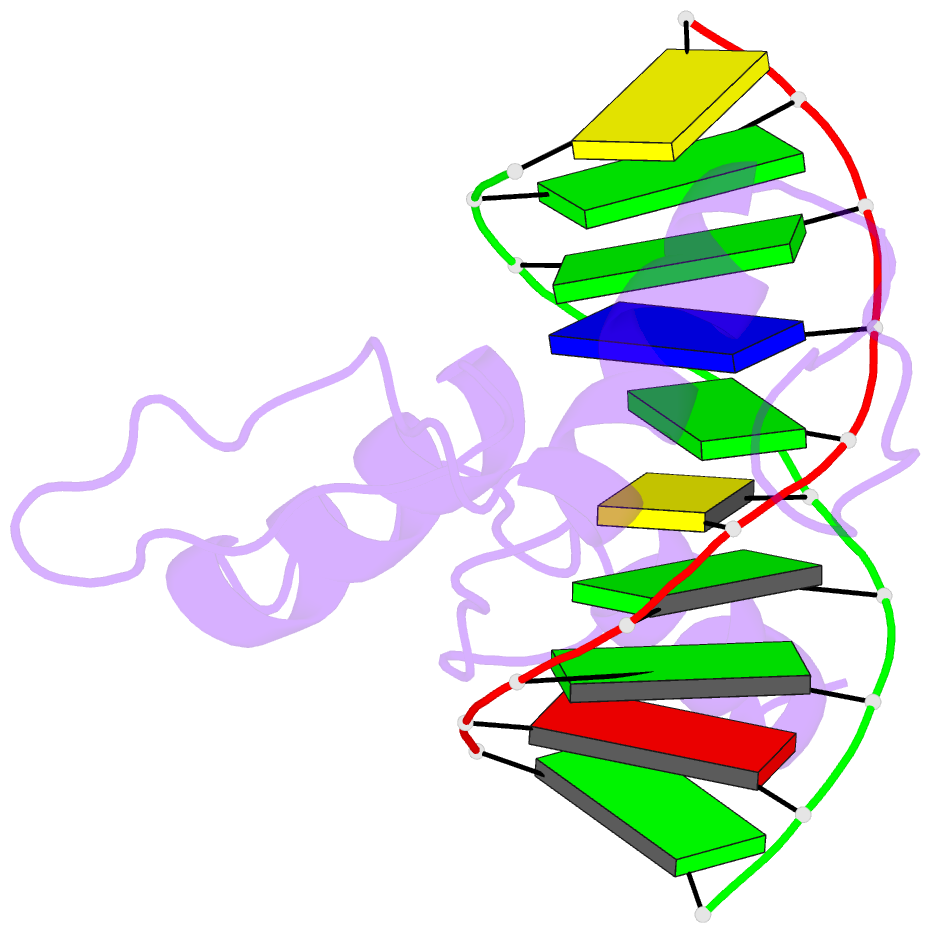
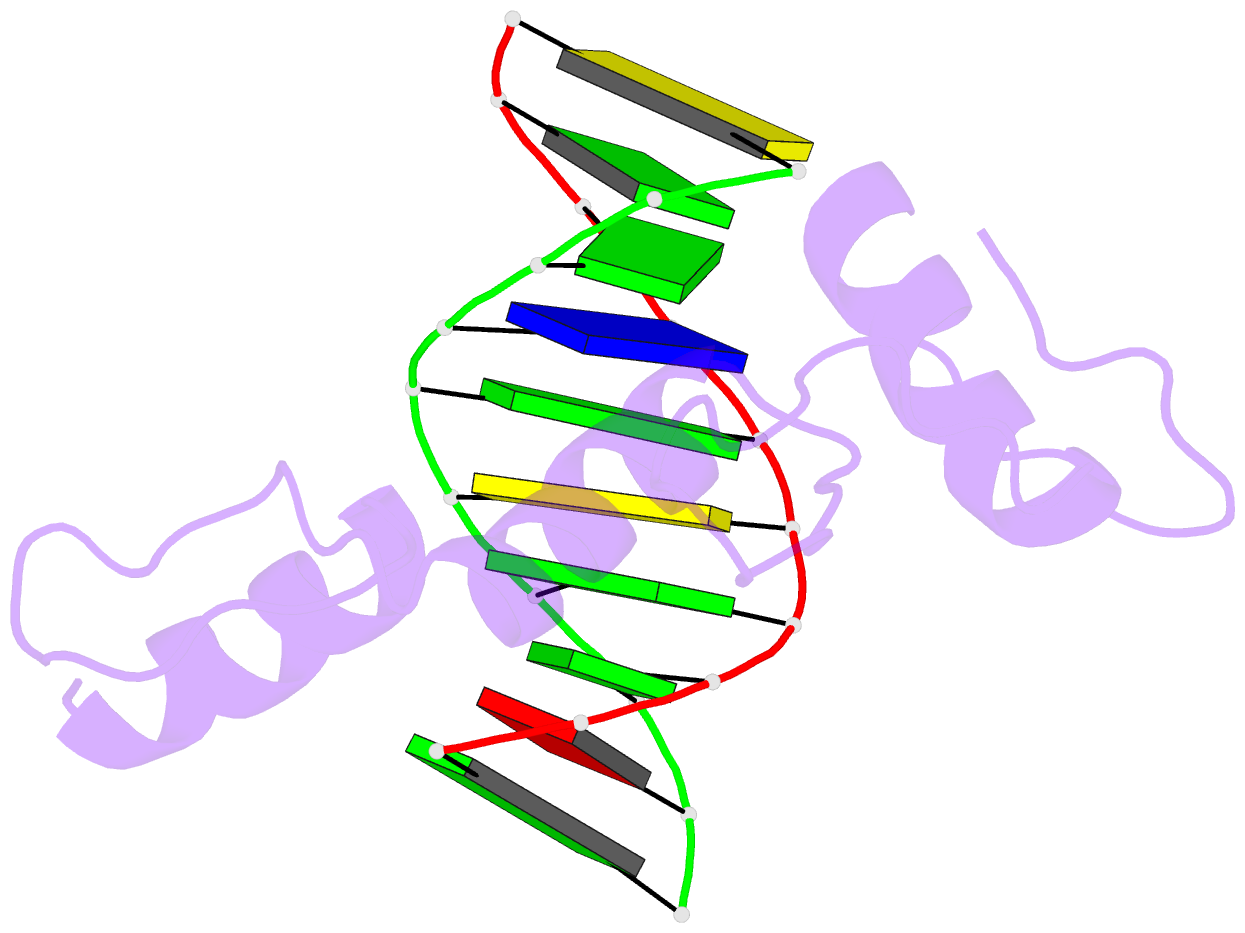
Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
-
5keb;
SNAP-derived features in text and
JSON formats
- Class
- transcription factor-DNA
- Method
- X-ray (2.453 Å)
- Summary
- Mouse klf4 znf1-3 (e446d) and cpg-cpg sequence DNA
complex structure: form ii
- Reference
-
Hashimoto H, Wang D, Steves AN, Jin P, Blumenthal RM,
Zhang X, Cheng X (2016): "Distinctive
Klf4 mutants determine preference for DNA methylation
status." Nucleic Acids Res.,
44, 10177-10185. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkw774.
- Abstract
- Reprogramming of mammalian genome methylation is
critically important but poorly understood. Klf4, a
transcription factor directing reprogramming, contains a
DNA binding domain with three consecutive C2H2 zinc
fingers. Klf4 recognizes CpG or TpG within a specific
sequence. Mouse Klf4 DNA binding domain has roughly equal
affinity for methylated CpG or TpG, and slightly lower
affinity for unmodified CpG. The structural basis for this
key preference is unclear, though the side chain of Glu446
is known to contact the methyl group of 5-methylcytosine
(5mC) or thymine (5-methyluracil). We examined the role of
Glu446 by mutagenesis. Substituting Glu446 with aspartate
(E446D) resulted in preference for unmodified cytosine, due
to decreased affinity for 5mC. In contrast, substituting
Glu446 with proline (E446P) increased affinity for 5mC by
two orders of magnitude. Structural analysis revealed
hydrophobic interaction between the proline's aliphatic
cyclic structure and the 5-methyl group of the pyrimidine
(5mC or T). As in wild-type Klf4 (E446), the proline at
position 446 does not interact directly with either the 5mC
N4 nitrogen or the thymine O4 oxygen. In contrast, the
unmethylated cytosine's exocyclic N4 amino group
(NH<sub>2</sub>) and its ring carbon C5 atom
hydrogen bond directly with the aspartate carboxylate of
the E446D variant. Both of these interactions would provide
a preference for cytosine over thymine, and the latter one
could explain the E446D preference for unmethylated
cytosine. Finally, we evaluated the ability of these Klf4
mutants to regulate transcription of methylated and
unmethylated promoters in a luciferase reporter assay.