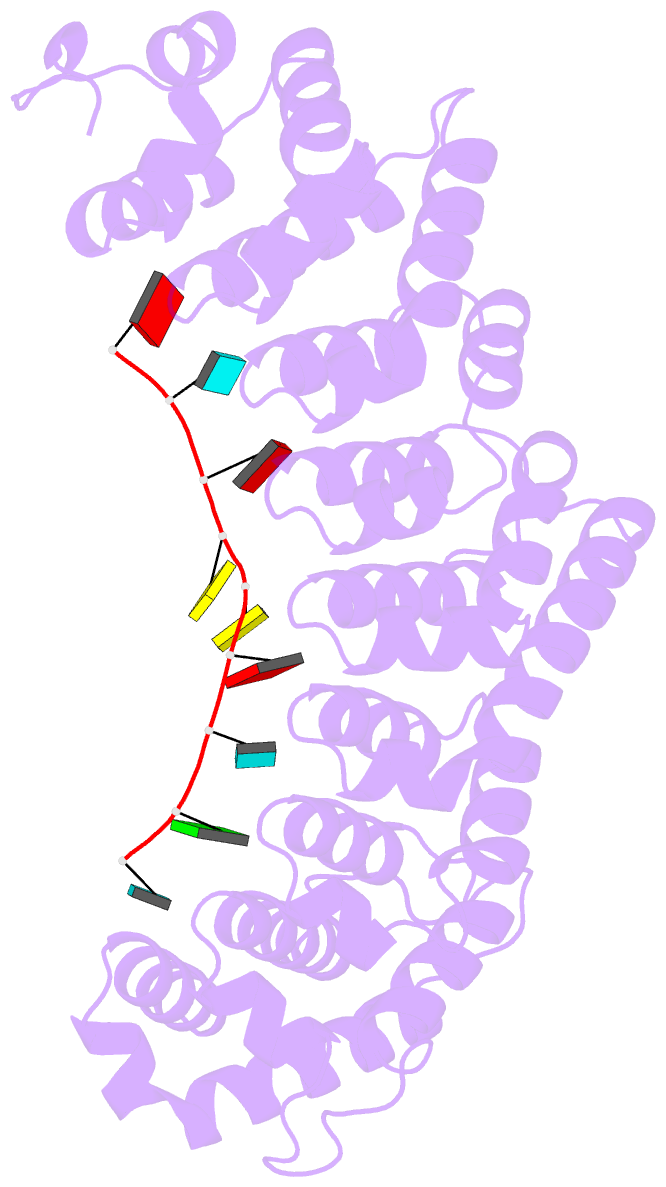
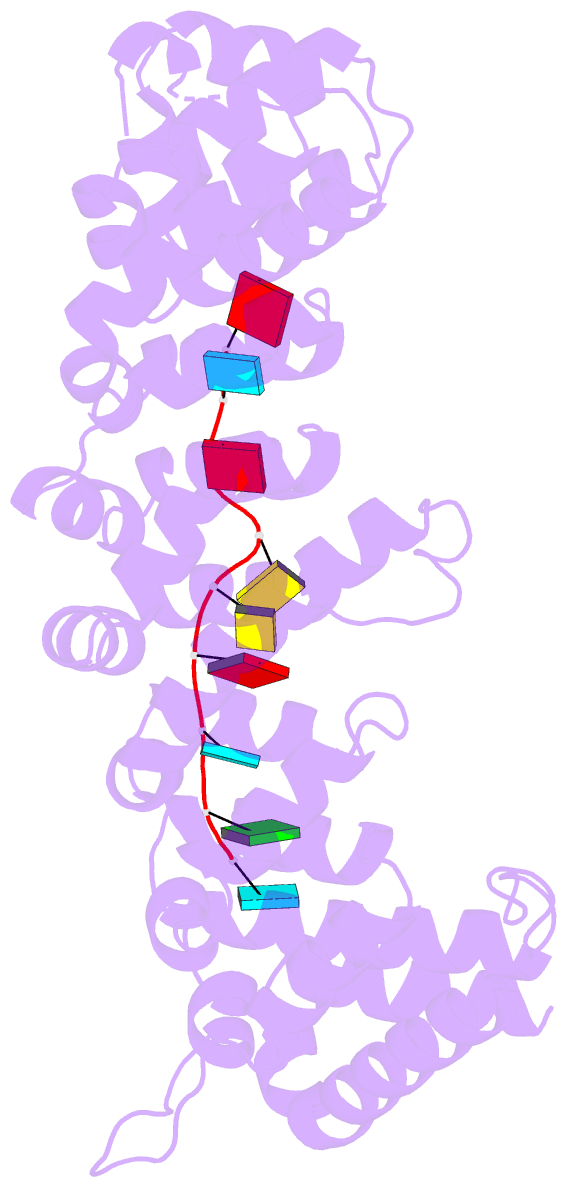
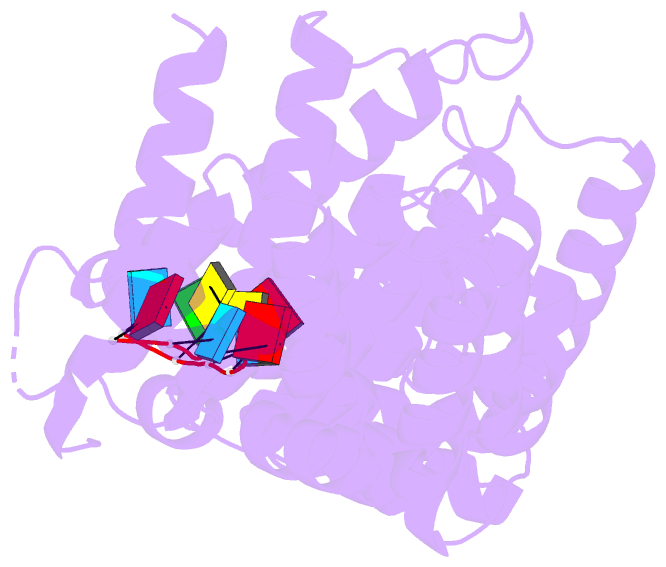
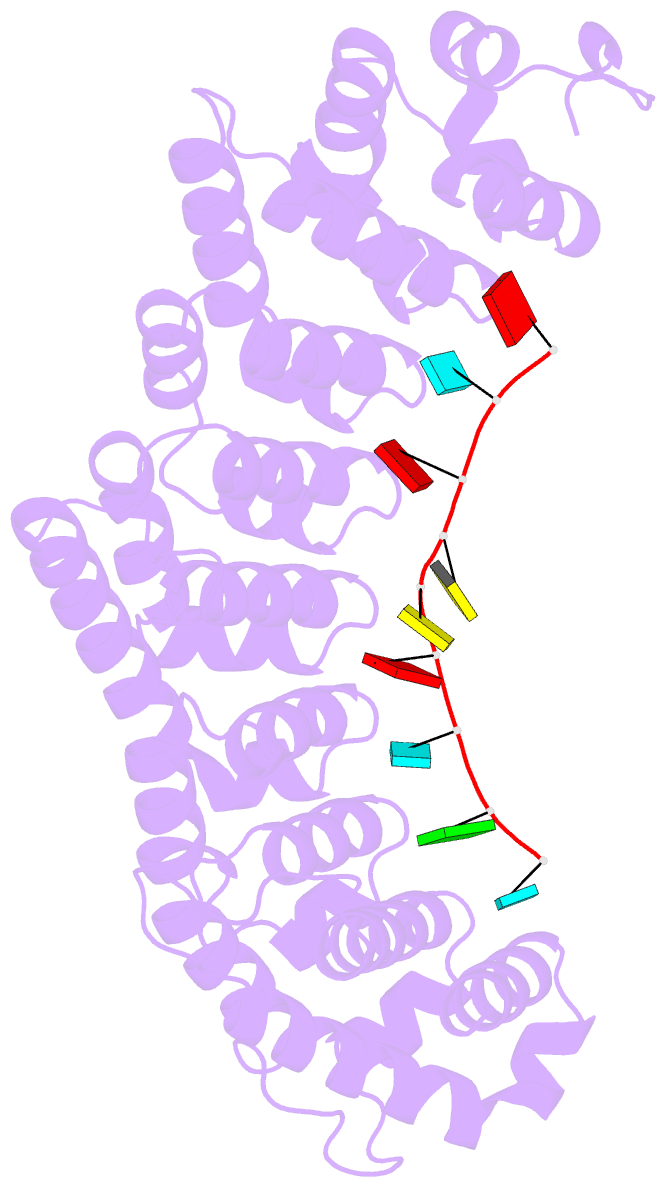
Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
-
3k5z;
SNAP-derived features in text and
JSON formats
- Class
- RNA-RNA binding protein
- Method
- X-ray (2.4 Å)
- Summary
- Crystal structure of fbf-2-gld-1 fbea g4a mutant
complex
- Reference
-
Wang Y, Opperman L, Wickens M, Hall TM (2009): "Structural
basis for specific recognition of multiple mRNA targets
by a PUF regulatory protein."
Proc.Natl.Acad.Sci.USA, 106,
20186-20191. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0812076106.
- Abstract
- Caenorhabditis elegans fem-3 binding factor (FBF) is a
founding member of the PUMILIO/FBF (PUF) family of mRNA
regulatory proteins. It regulates multiple mRNAs critical
for stem cell maintenance and germline development. Here,
we report crystal structures of FBF in complex with 6
different 9-nt RNA sequences, including elements from 4
natural mRNAs. These structures reveal that FBF binds to
conserved bases at positions 1-3 and 7-8. The key
specificity determinant of FBF vs. other PUF proteins lies
in positions 4-6. In FBF/RNA complexes, these bases stack
directly with one another and turn away from the
RNA-binding surface. A short region of FBF is sufficient to
impart its unique specificity and lies directly opposite
the flipped bases. We suggest that this region imposes a
flattened curvature on the protein; hence, the requirement
for the additional nucleotide. The principles of FBF/RNA
recognition suggest a general mechanism by which PUF
proteins recognize distinct families of RNAs yet exploit
very nearly identical atomic contacts in doing so.