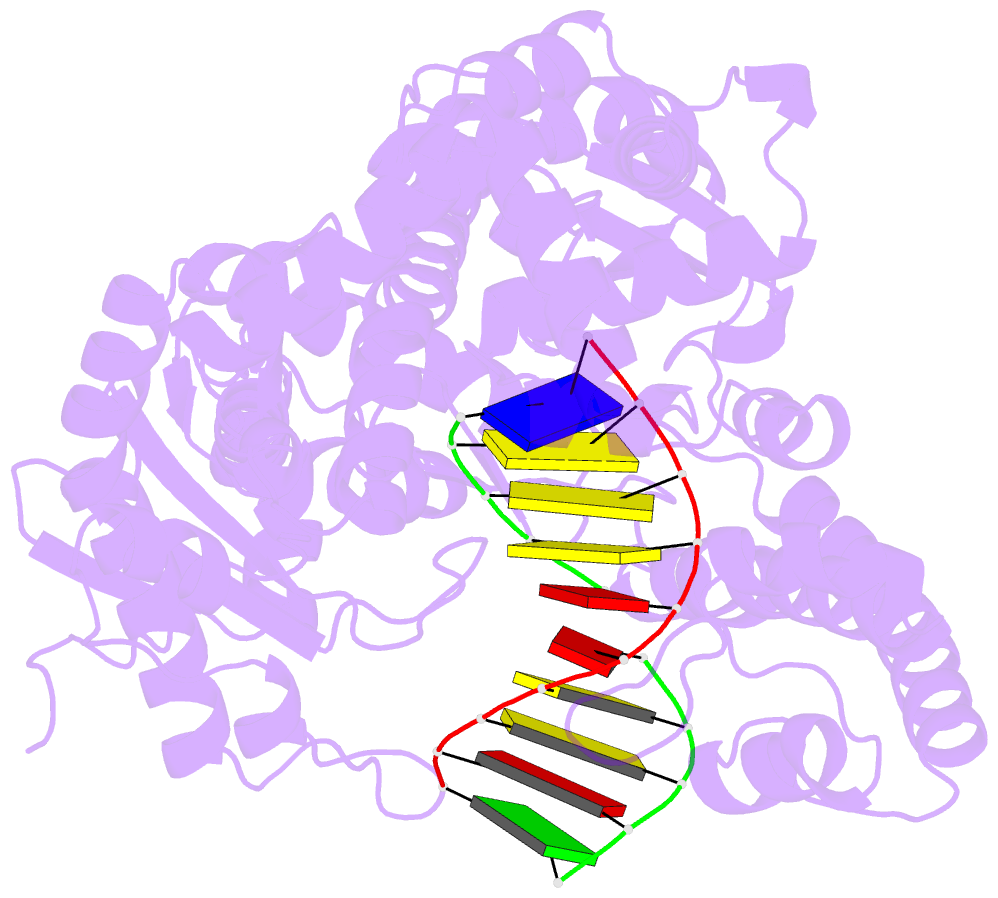
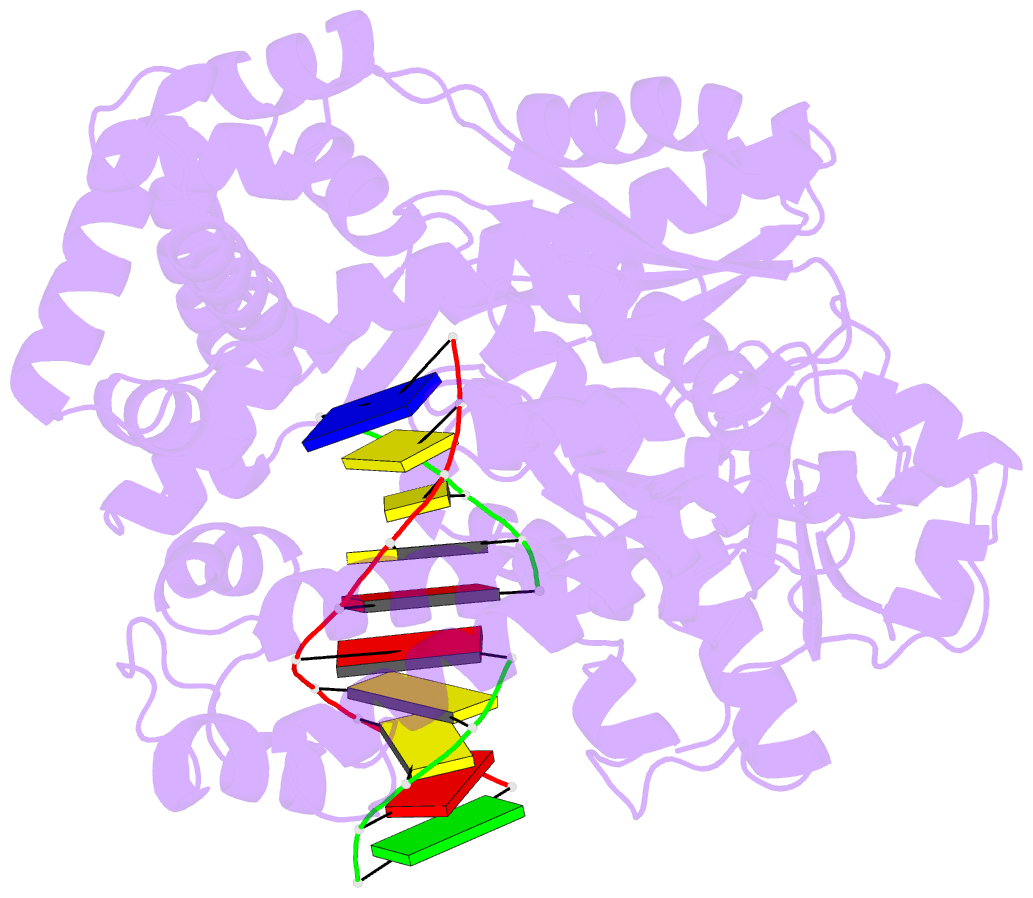
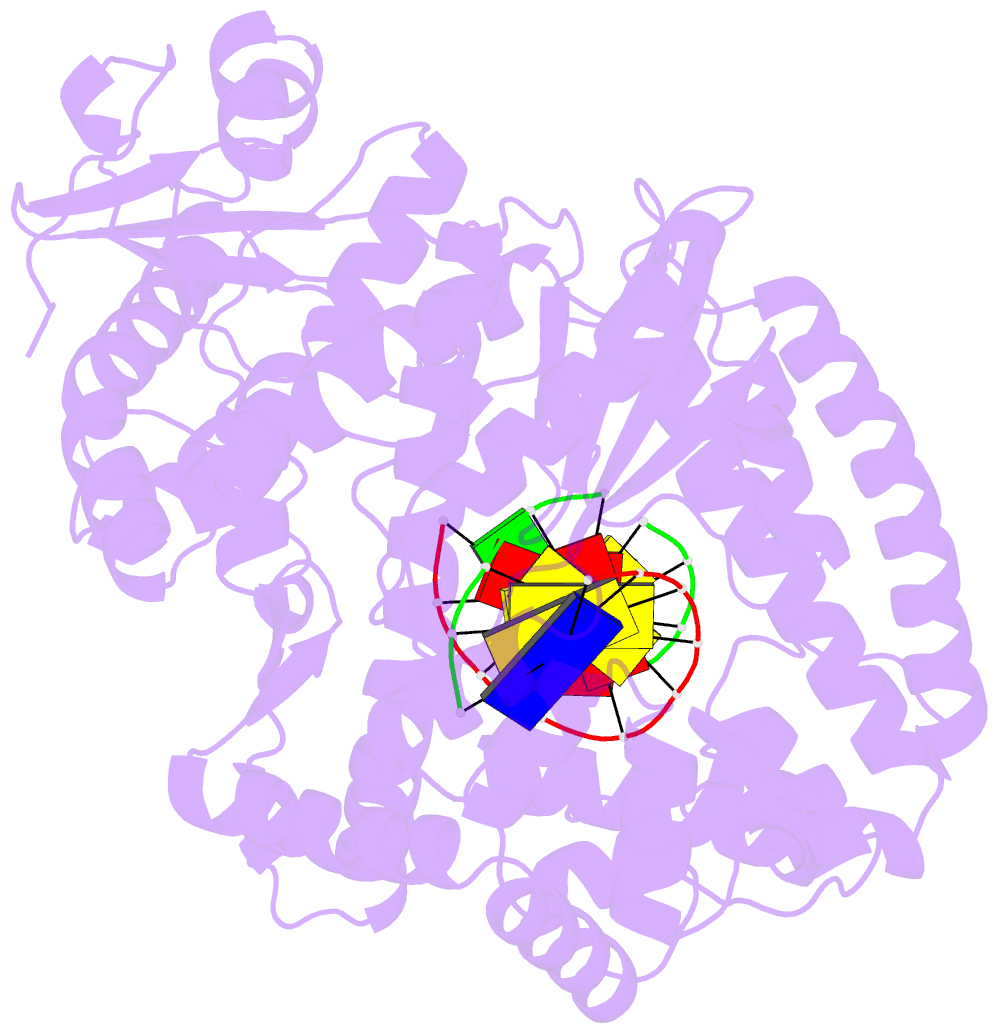
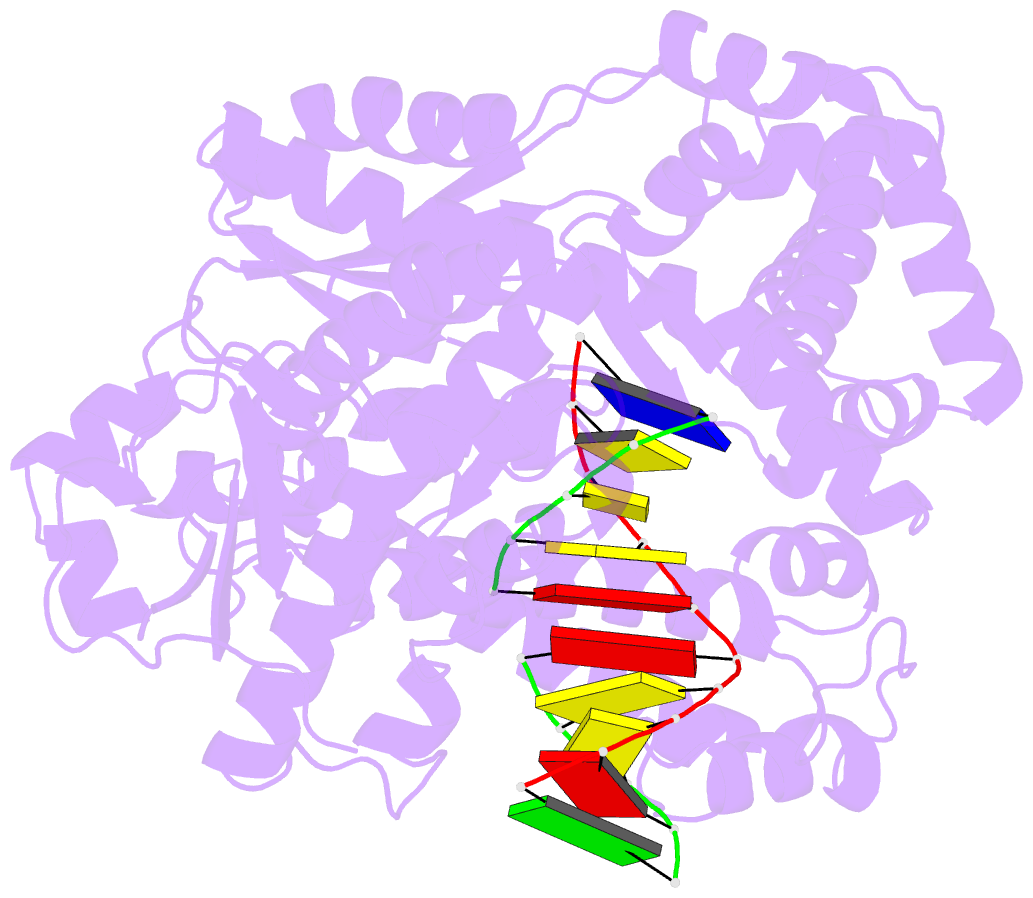
Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
-
2y1j;
SNAP-derived features in text and
JSON formats
- Class
- transferase-DNA
- Method
- X-ray (2.15 Å)
- Summary
- Crystal structure of a r-diastereomer analogue of the
spore photoproduct in complex with fragment DNA polymerase
i from bacillus stearothermophilus
- Reference
-
Heil K, Kneuttinger AC, Schneider S, Lischke U, Carell T
(2011): "Crystal
Structures and Repair Studies Reveal the Identity and the
Base-Pairing Properties of the Uv-Induced Spore
Photoproduct DNA Lesion." Chemistry,
17, 9651. doi: 10.1002/CHEM.201100177.
- Abstract
- UV light is one of the major causes of DNA damage. In
spore DNA, due to an unusual packing of the genetic
material, a special spore photoproduct lesion (SP lesion)
is formed, which is repaired by the enzyme spore
photoproduct lyase (Spl), a radical S-adenosylmethionine
(SAM) enzyme. We report here the synthesis and DNA
incorporation of a DNA SP lesion analogue lacking the
phosphodiester backbone. The oligonucleotides were used for
repair studies and they were cocrystallized with a
polymerase enzyme as a template to clarify the
configuration of the SP lesion and to provide information
about the base-pairing properties of the lesion. The
structural analysis together with repair studies allowed us
to clarify the identity of the preferentially repaired
lesion diastereoisomer.