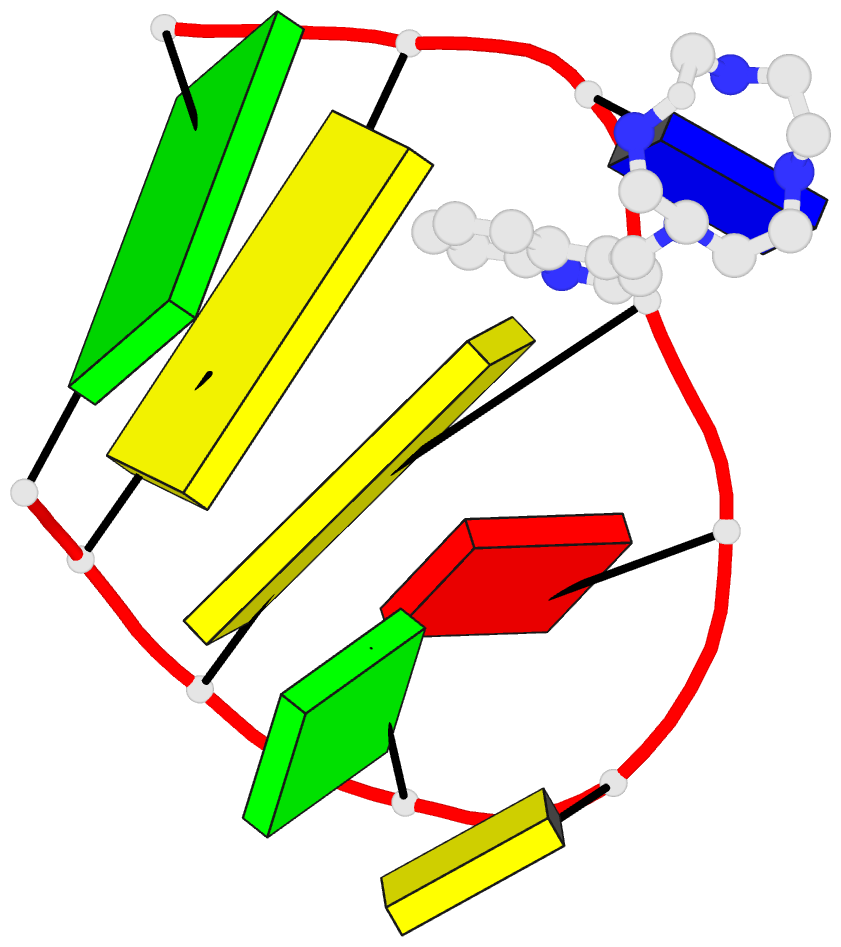
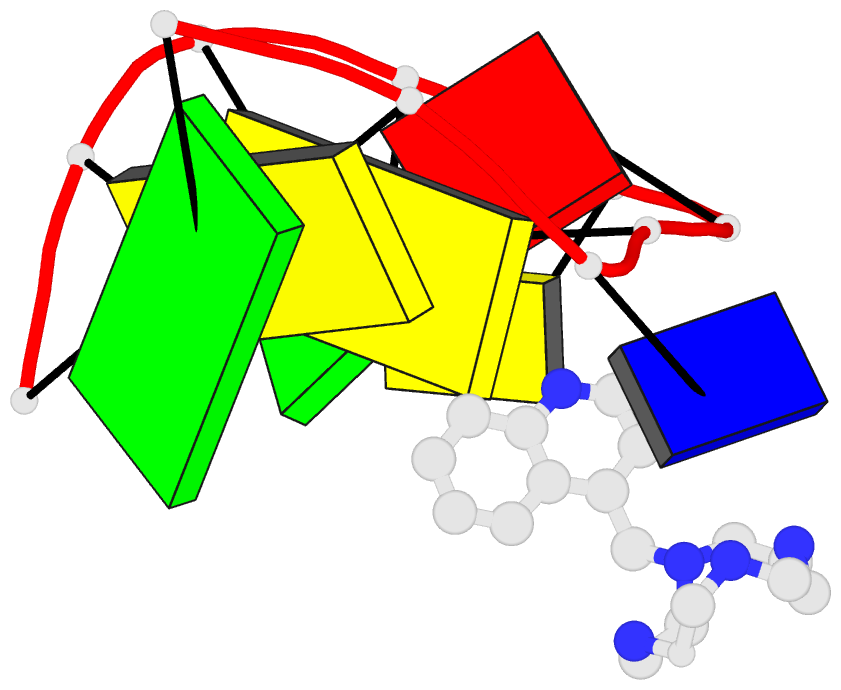
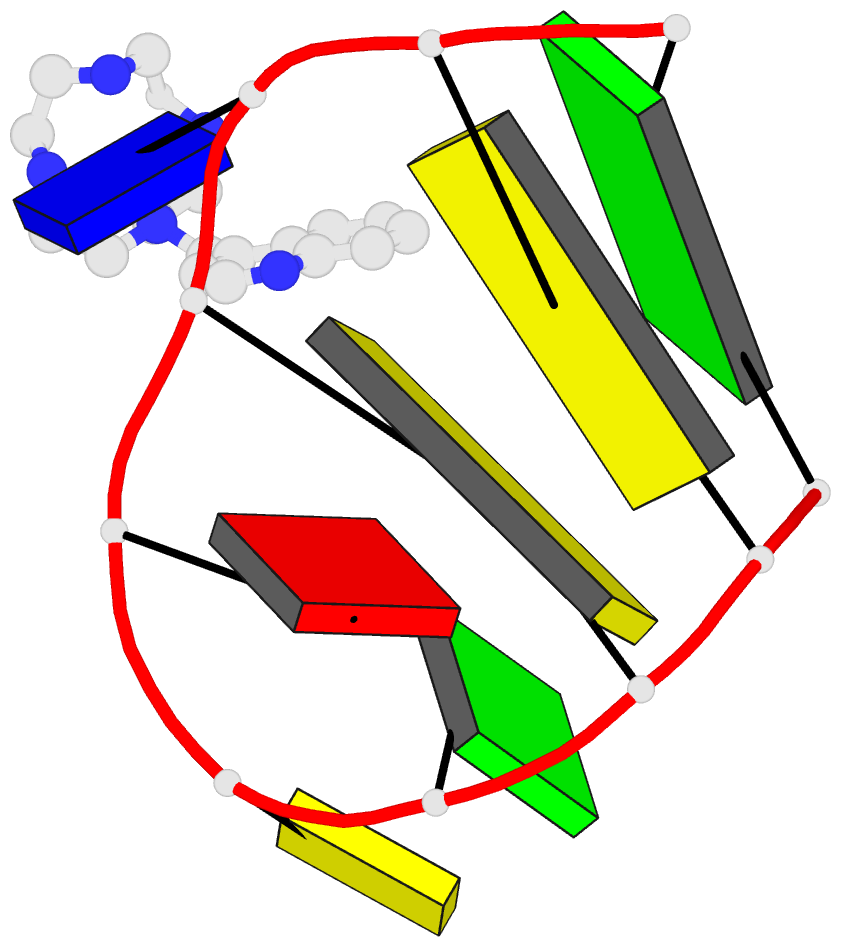
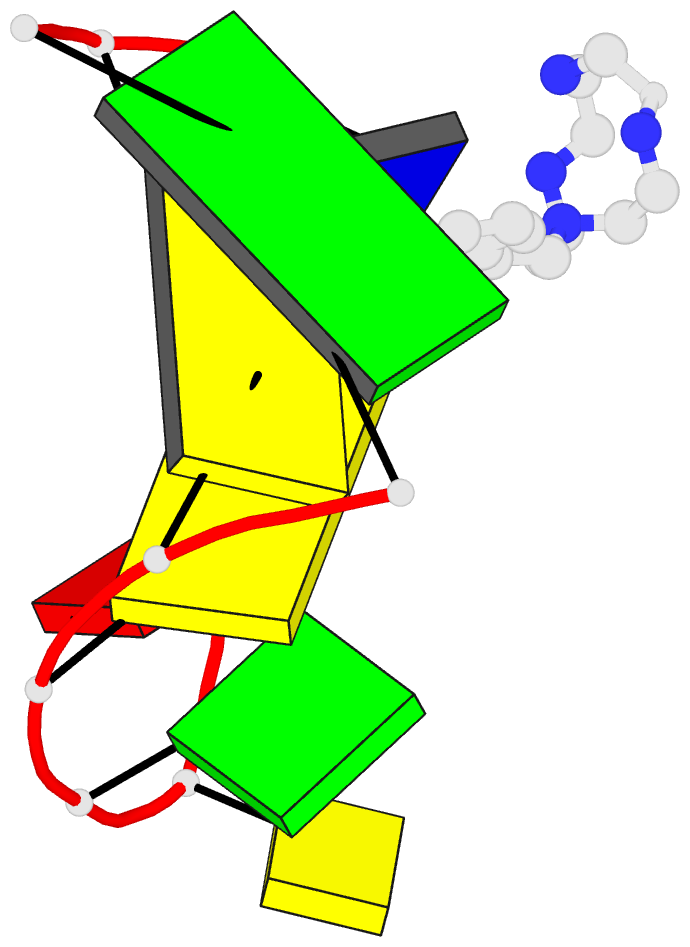
Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
-
2loa;
SNAP-derived features in text and
JSON formats
- Class
- DNA
- Method
- NMR
- Summary
- Structural basis for bifunctional zn(ii) macrocyclic
complex recognition of thymine bulges in DNA
- Reference
-
Del Mundo IM, Siters KE, Fountain MA, Morrow JR (2012):
"Structural
Basis for Bifunctional Zinc(II) Macrocyclic Complex
Recognition of Thymine Bulges in DNA."
Inorg.Chem., 51, 5444-5457.
doi: 10.1021/ic3004245.
- Abstract
- The zinc(II) complex of
1-(4-quinoylyl)methyl-1,4,7,10-tetraazacyclododecane (cy4q)
binds selectively to thymine bulges in DNA and to a uracil
bulge in RNA. Binding constants are in the low-micromolar
range for thymine bulges in the stems of hairpins, for a
thymine bulge in a DNA duplex, and for a uracil bulge in an
RNA hairpin. Binding studies of Zn(cy4q) to a series of
hairpins containing thymine bulges with different flanking
bases showed that the complex had a moderate selectivity
for thymine bulges with neighboring purines. The
dissociation constants of the most strongly bound
Zn(cy4q)-DNA thymine bulge adducts were 100-fold tighter
than similar sequences with fully complementary stems or
than bulges containing cytosine, guanine, or adenine. In
order to probe the role of the pendent group, three
additional zinc(II) complexes containing
1,4,7,10-tetraazacyclododecane (cyclen) with aromatic
pendent groups were studied for binding to DNA including
1-(2-quinolyl)methyl-1,4,7,10-tetraazacyclododecane (cy2q),
1-(4-biphenyl)methyl-1,4,7,10-tetraazacyclododecane (cybp),
and
5-(1,4,7,10-tetraazacyclododecan-1-ylsulfonyl)-N,N-dimethylnaphthalen-1-amine
(dsc). The Zn(cybp) complex binds with moderate affinity
but little selectivity to DNA hairpins with thymine bulges
and to DNA lacking bulges. Similarly, Zn(dsc) binds weakly
both to thymine bulges and hairpins with fully
complementary stems. The zinc(II) complex of cy2q has the
2-quinolyl moiety bound to the Zn(II) center, as shown by
(1)H NMR spectroscopy and pH-potentiometric titrations. As
a consequence, only weak (500 μM) binding is observed to
DNA with no appreciable selectivity. An NMR structure of a
thymine-bulge-containing hairpin shows that the thymine is
extrahelical but rotated toward the major groove. NMR data
for Zn(cy4q) bound to DNA containing a thymine bulge is
consistent with binding of the zinc(II) complex to the
thymine N3(-) and stacking of the quinoline on top of the
thymine. The thymine-bulge bound zinc(II) complex is
pointed into the major groove, and there are interactions
with the guanine positioned 5' to the thymine bulge.