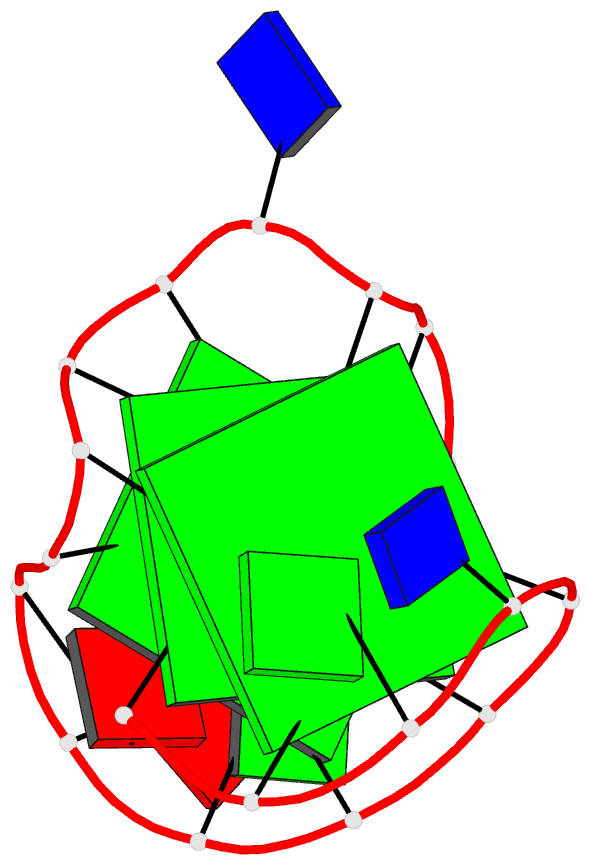
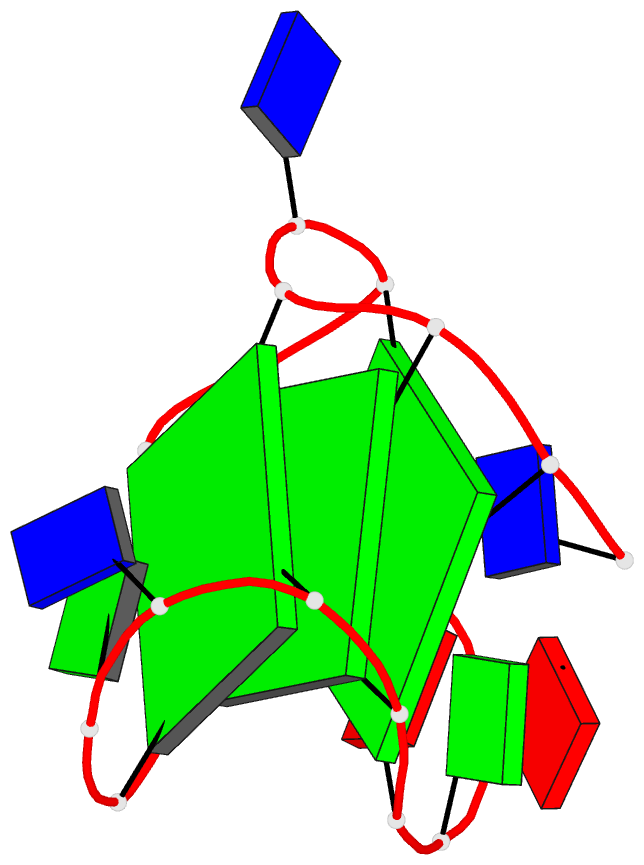
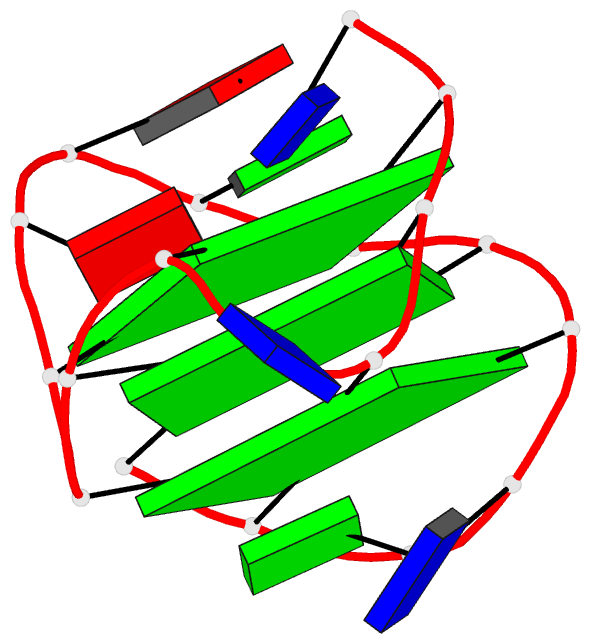
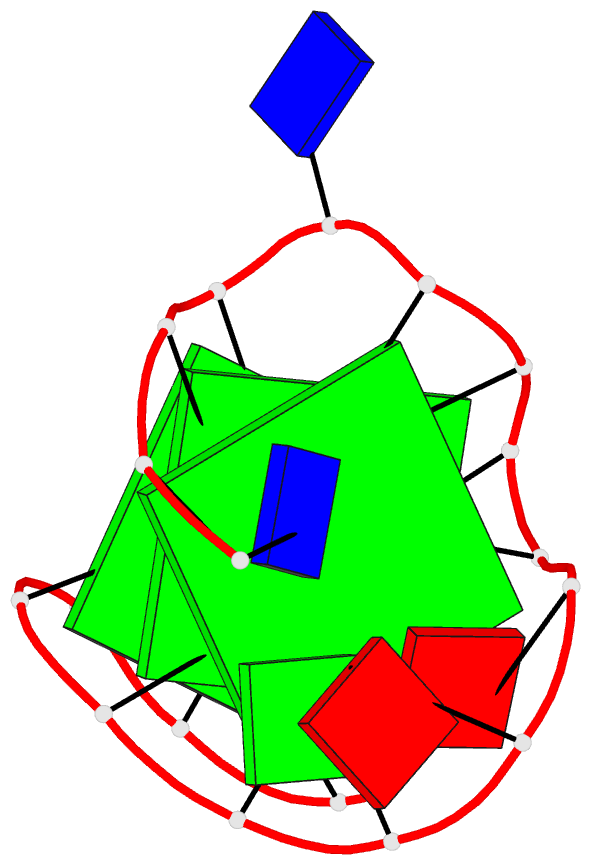
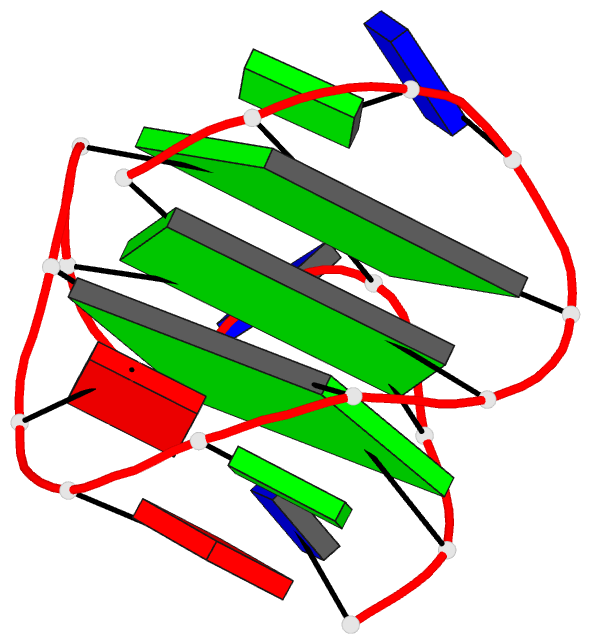
Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
-
2kpr;
SNAP-derived features in text and
JSON formats
- Class
- DNA
- Method
- NMR
- Summary
- Monomeric intronic human chl1 gene quadruplex DNA NMR,
17 structures
- Reference
-
Kuryavyi V, Patel DJ (2010): "Solution
Structure of a Unique G-Quadruplex Scaffold Adopted by a
Guanosine-Rich Human Intronic Sequence."
Structure, 18, 73-82. doi:
10.1016/j.str.2009.10.015.
- Abstract
- We report on the solution structure of an unprecedented
intramolecular G-quadruplex formed by the guanosine-rich
human chl1 intronic d(G(3)-N-G(4)-N(2)-G(4)-N-G(3)-N)
19-mer sequence in K(+)-containing solution. This
G-quadruplex, composed of three stacked G-tetrads
containing four syn guanines, represents a new folding
topology with two unique conformational features. The first
guanosine is positioned within the central G-tetrad, in
contrast to all previous structures of unimolecular
G-quadruplexes, where the first guanosine is part of an
outermost G-tetrad. In addition, a V-shaped loop, spanning
three G-tetrad planes, contains no bridging nucleotides.
The G-quadruplex scaffold is stabilized by a T*G*A triple
stacked over the G-tetrad at one end and an unpaired
guanosine stacked over the G-tetrad at the other end.
Finally, the chl1 intronic DNA G-quadruplex scaffold
contains a guanosine base intercalated between an extended
G-G step, a feature observed in common with the catalytic
site of group I introns. This unique structural scaffold
provides a highly specific platform for the future design
of ligands specifically targeted to intronic G-quadruplex
platforms.