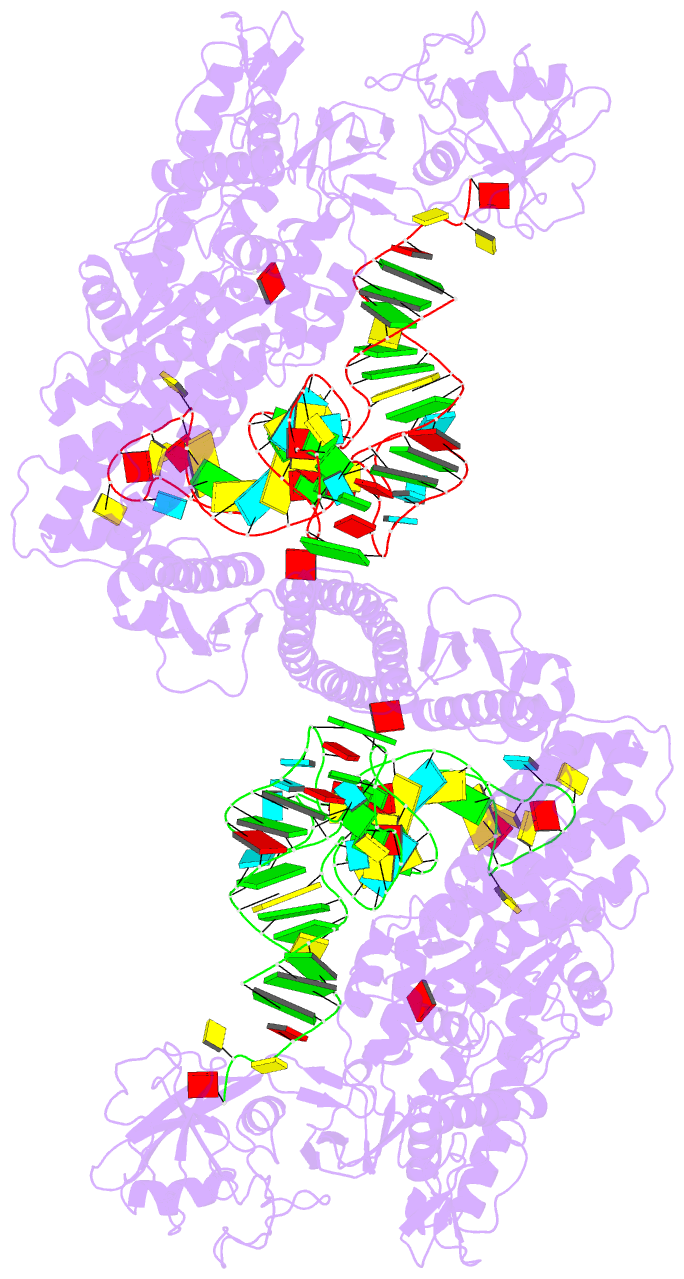
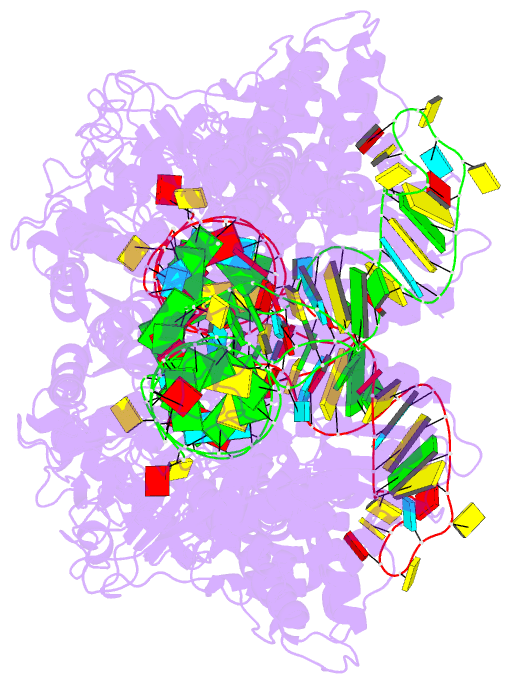
Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
-
1ivs;
SNAP-derived features in text and
JSON formats
- Class
- ligase-RNA
- Method
- X-ray (2.9 Å)
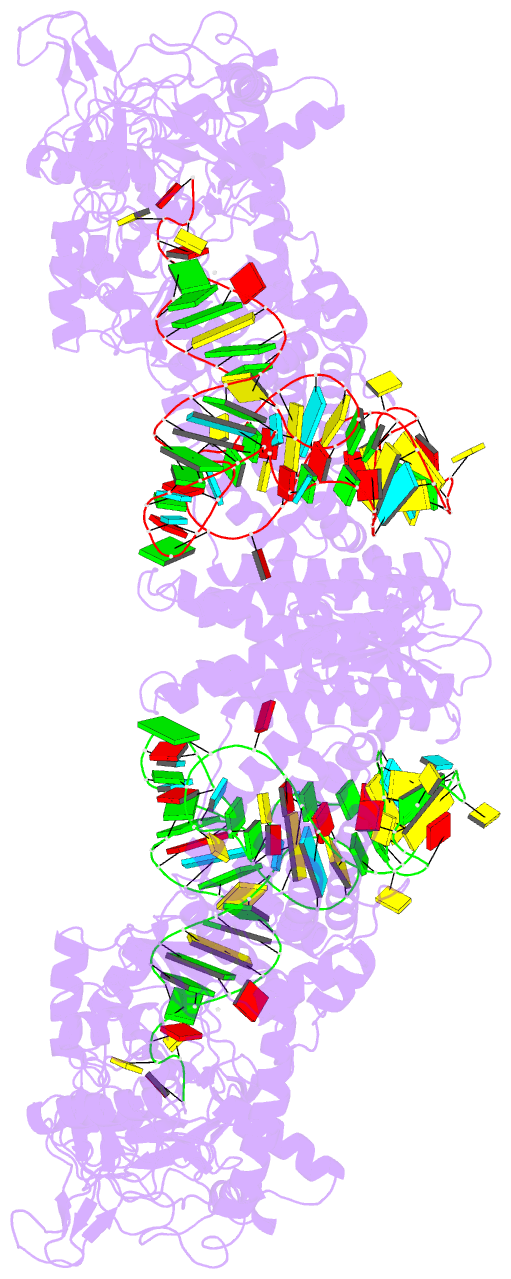
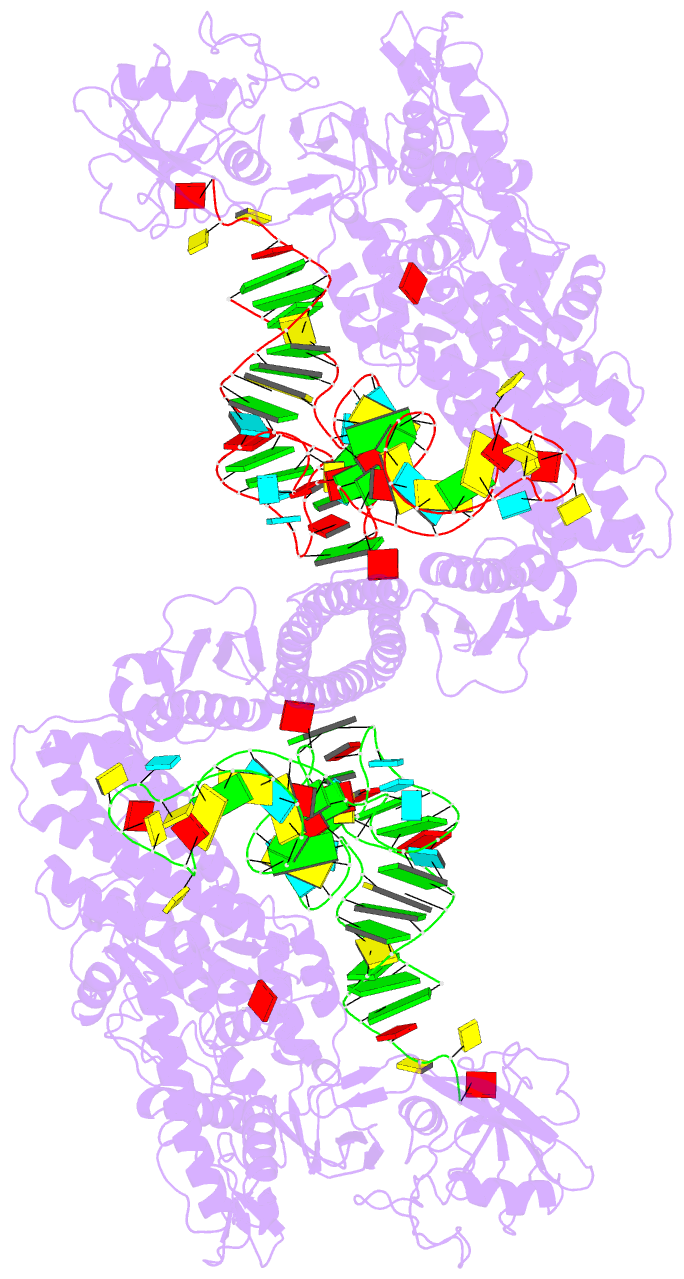
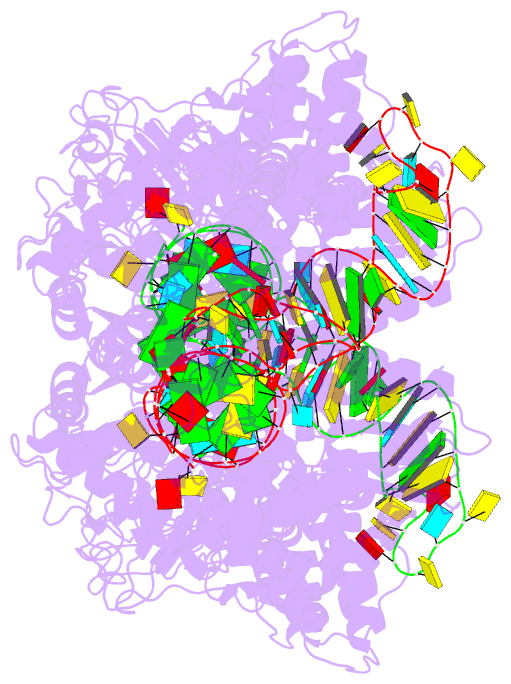
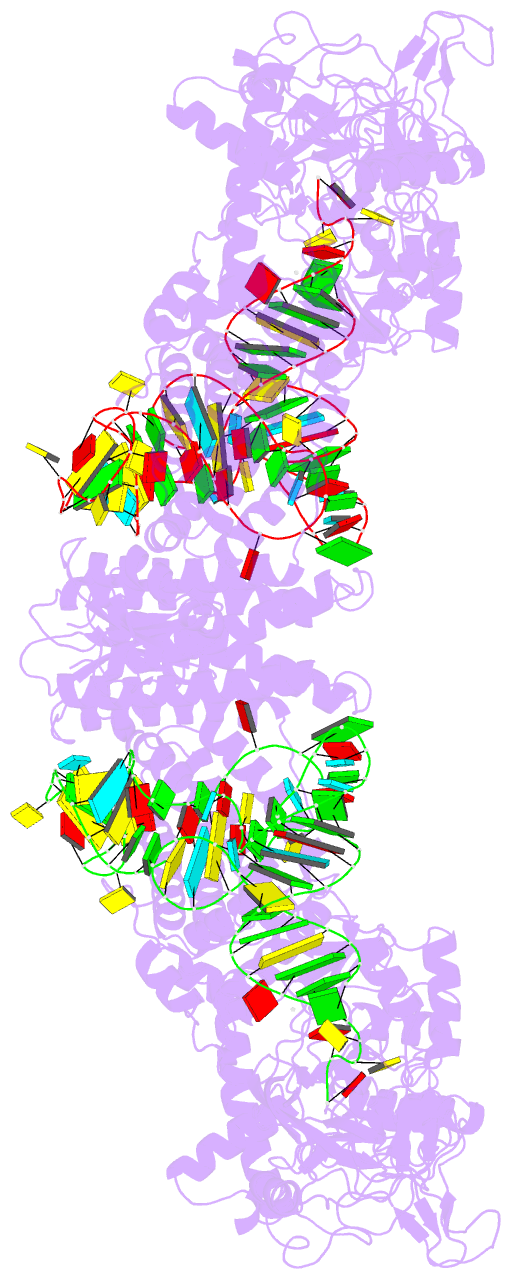
- Summary
- Crystal structure of thermus thermophilus valyl-trna
synthetase complexed with trna(val) and valyl-adenylate
analogue
- Reference
-
Fukai S, Nureki O, Sekine S-I, Shimada A, Vassylyev DG,
Yokoyama S (2003): "Mechanism
of molecular interactions for tRNA(Val) recognition by
valyl-tRNA synthetase." RNA,
9, 100-111. doi: 10.1261/rna.2760703.
- Abstract
- The molecular interactions between valyl-tRNA
synthetase (ValRS) and tRNA(Val), with the C34-A35-C36
anticodon, from Thermus thermophilus were studied by
crystallographic analysis and structure-based mutagenesis.
In the ValRS-bound structure of tRNA(Val), the successive
A35-C36 residues (the major identity elements) of tRNA(Val)
are base-stacked upon each other, and fit into a pocket on
the alpha-helix bundle domain of ValRS. Hydrogen bonds are
formed between ValRS and A35-C36 of tRNA(Val) in a
base-specific manner. The C-terminal coiled-coil domain of
ValRS interacts electrostatically with A20 and
hydrophobically with the G19*C56 tertiary base pair. The
loss of these interactions by the deletion of the
coiled-coil domain of ValRS increased the K(M) value for
tRNA(Val) 28-fold and decreased the k(cat) value 19-fold in
the aminoacylation. The tRNA(Val) K(M) and k(cat) values
were increased 21-fold and decreased 32-fold, respectively,
by the disruption of the G18*U55 and G19*C56 tertiary base
pairs, which associate the D- and T-loops for the formation
of the L-shaped tRNA structure. Therefore, the coiled-coil
domain of ValRS is likely to stabilize the L-shaped tRNA
structure during the aminoacylation reaction.