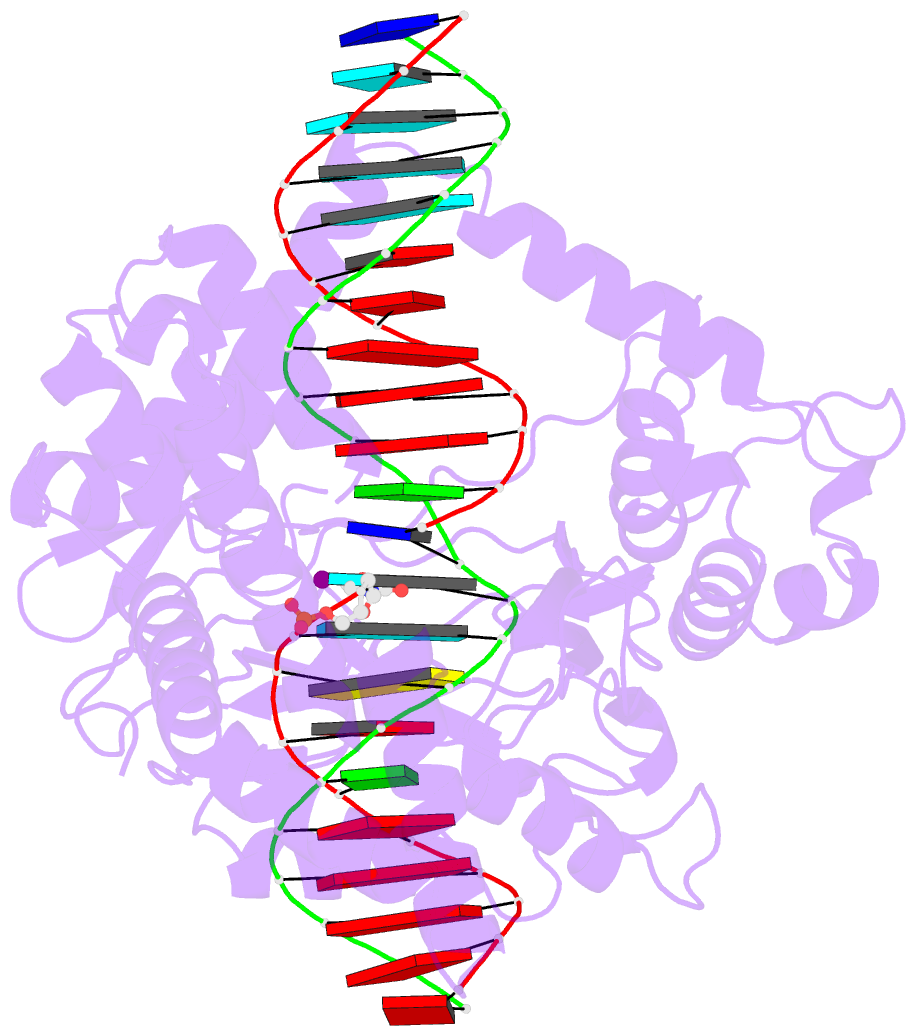
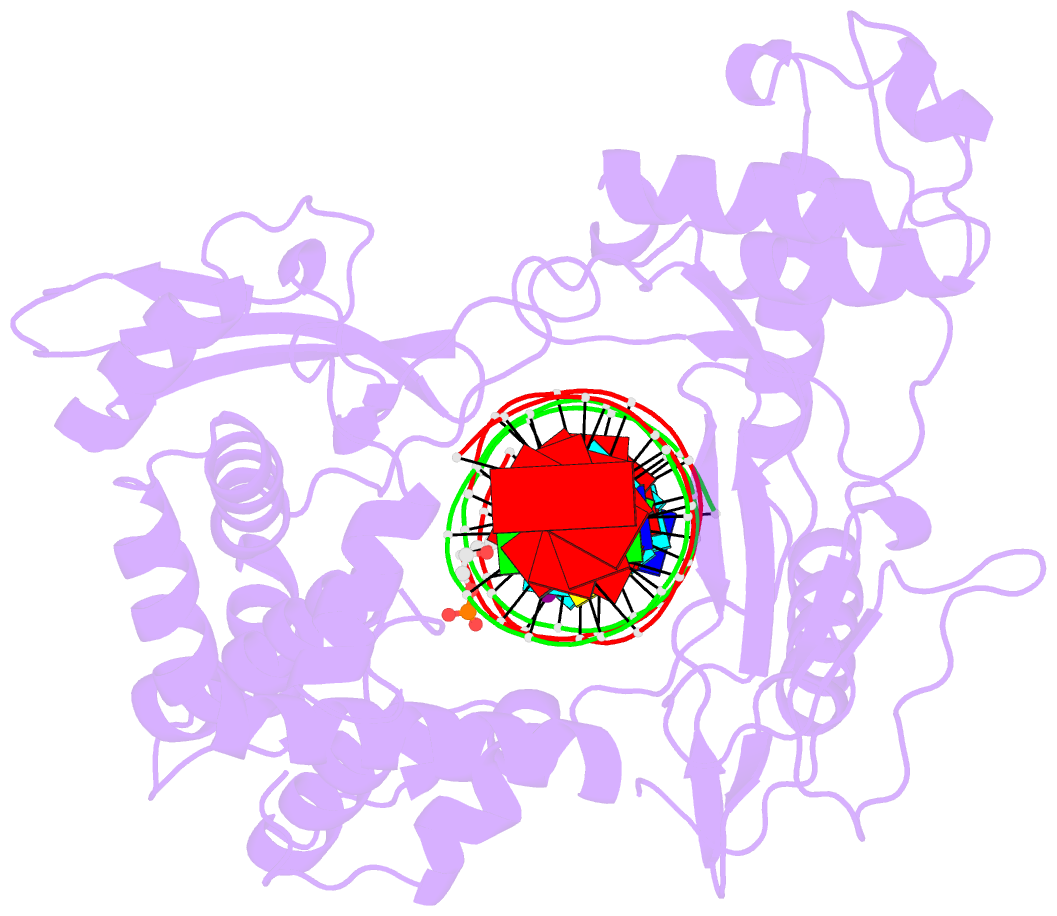
Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
-
1a31;
SNAP-derived features in text and
JSON formats
- Class
- isomerase-DNA
- Method
- X-ray (2.1 Å)
- Summary
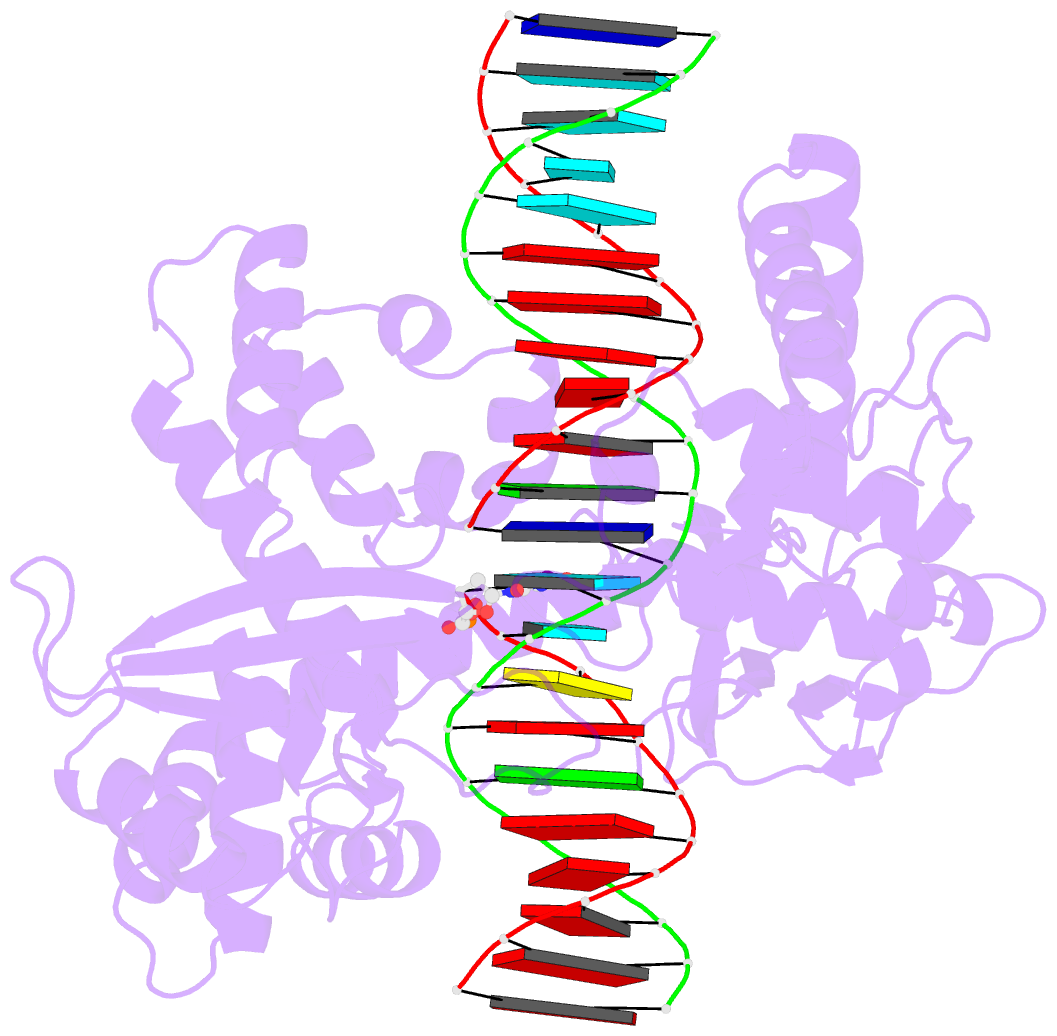
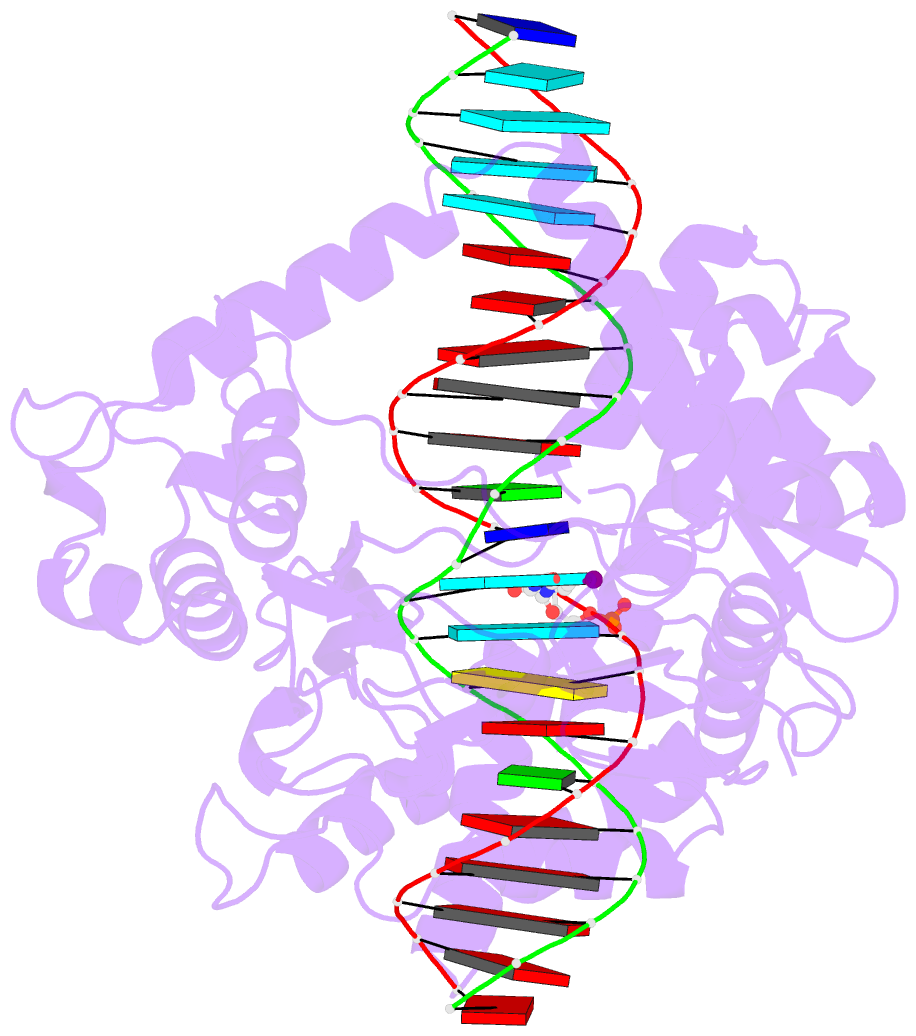
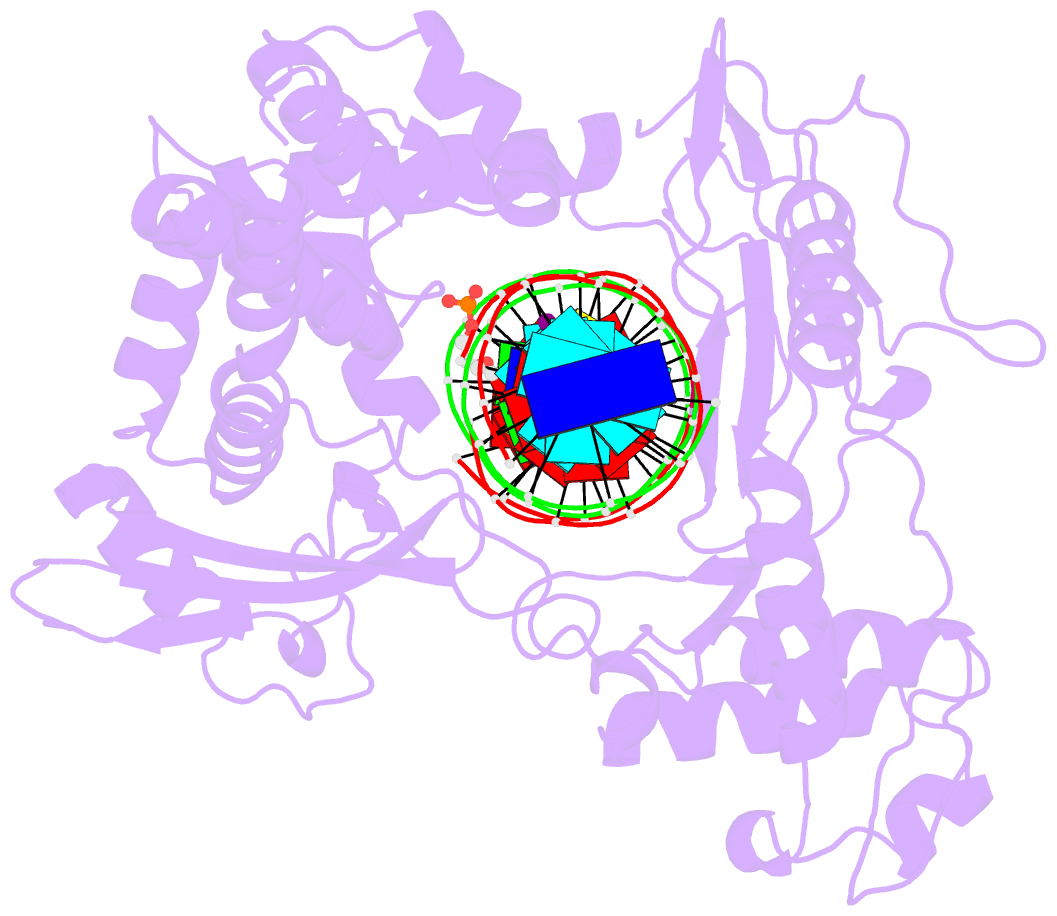
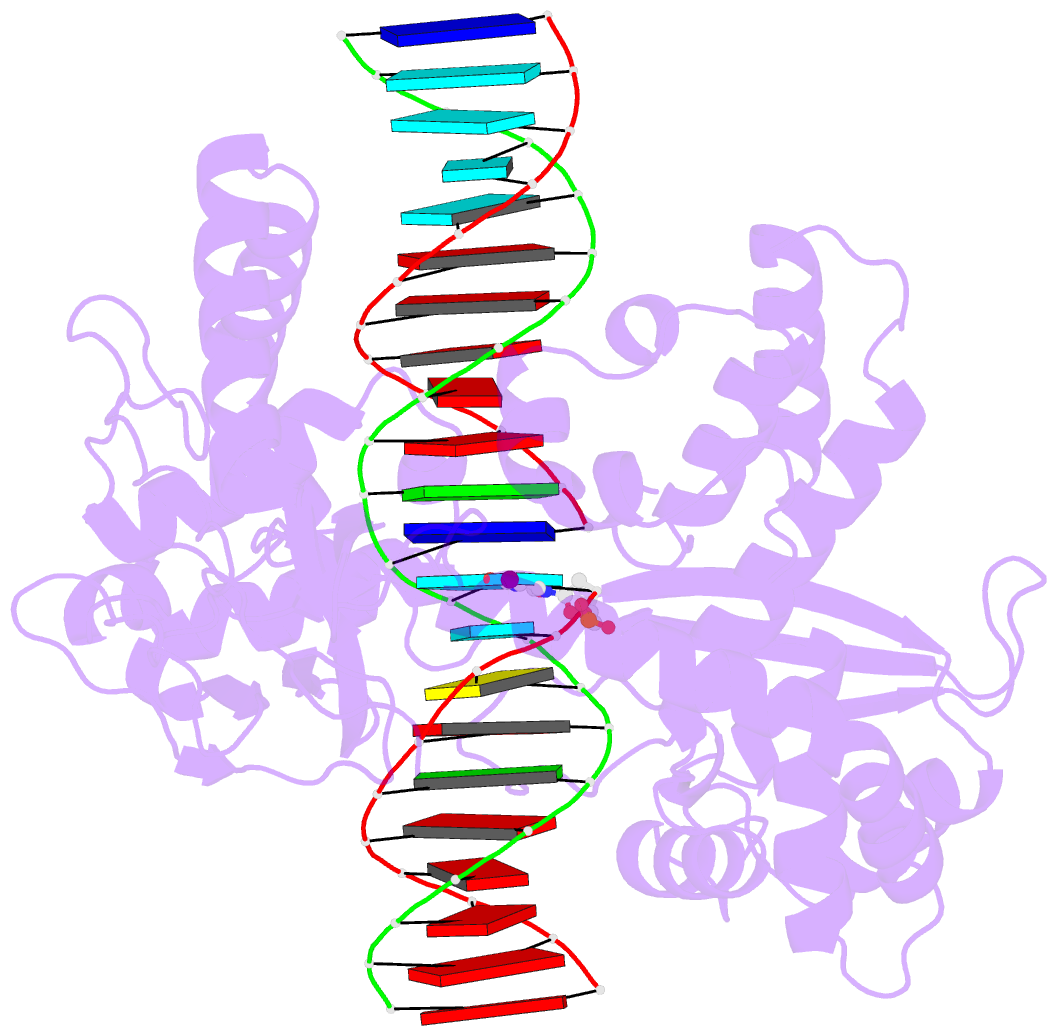
- Human reconstituted DNA topoisomerase i in covalent
complex with a 22 base pair DNA duplex
- Reference
-
Redinbo MR, Stewart L, Kuhn P, Champoux JJ, Hol WG
(1998): "Crystal
structures of human topoisomerase I in covalent and
noncovalent complexes with DNA." Science,
279, 1504-1513. doi: 10.1126/science.279.5356.1504.
- Abstract
- Topoisomerases I promote the relaxation of DNA
superhelical tension by introducing a transient
single-stranded break in duplex DNA and are vital for the
processes of replication, transcription, and recombination.
The crystal structures at 2.1 and 2.5 angstrom resolution
of reconstituted human topoisomerase I comprising the core
and carboxyl-terminal domains in covalent and noncovalent
complexes with 22-base pair DNA duplexes reveal an enzyme
that "clamps" around essentially B-form DNA. The core
domain and the first eight residues of the
carboxyl-terminal domain of the enzyme, including the
active-site nucleophile tyrosine-723, share significant
structural similarity with the bacteriophage family of DNA
integrases. A binding mode for the anticancer drug
camptothecin is proposed on the basis of chemical and
biochemical information combined with these
three-dimensional structures of topoisomerase I-DNA
complexes.