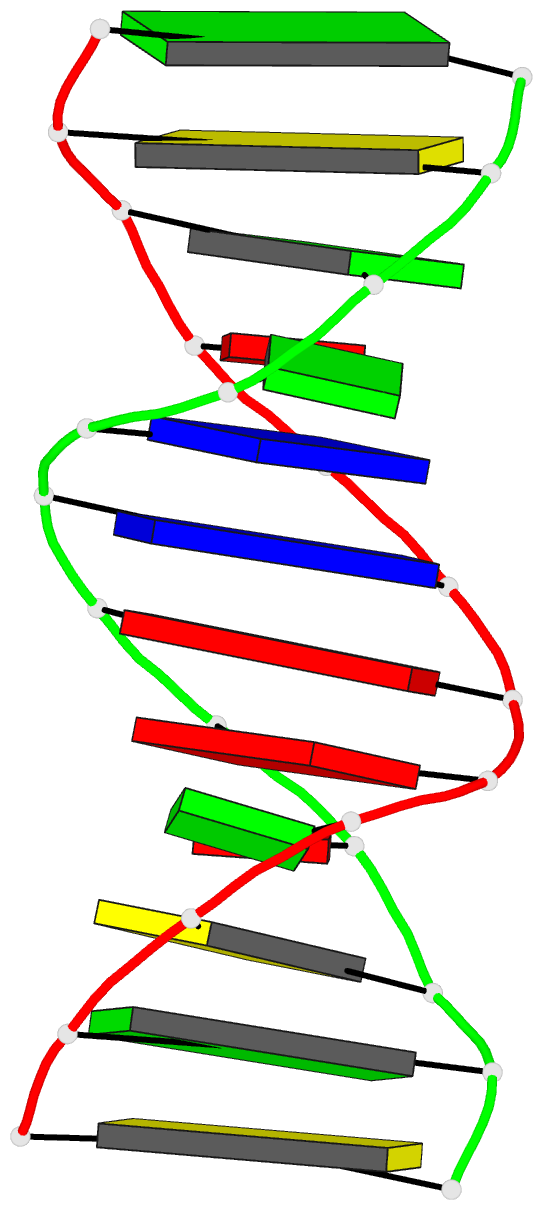
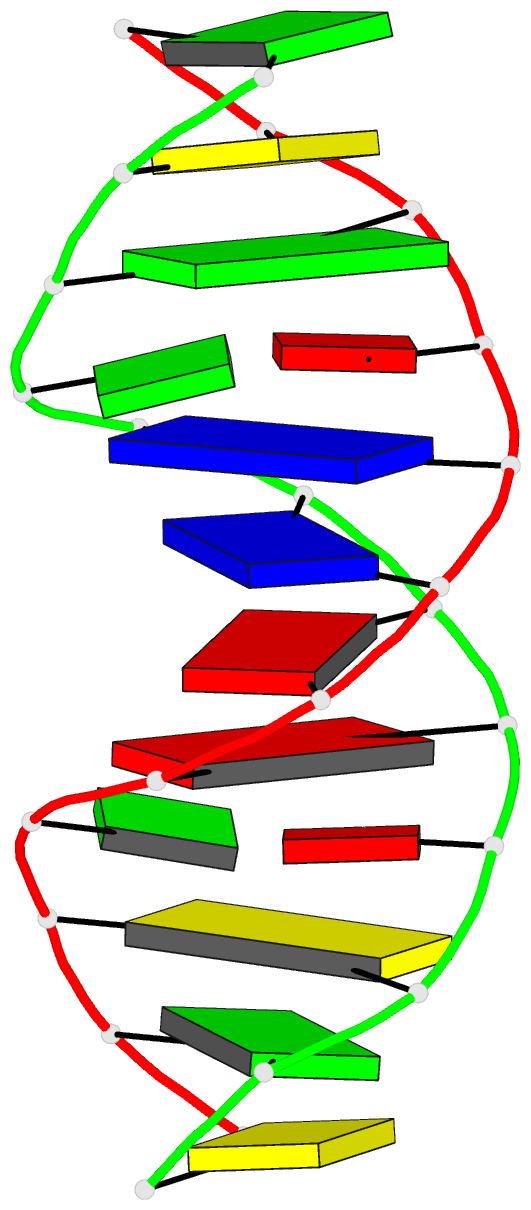
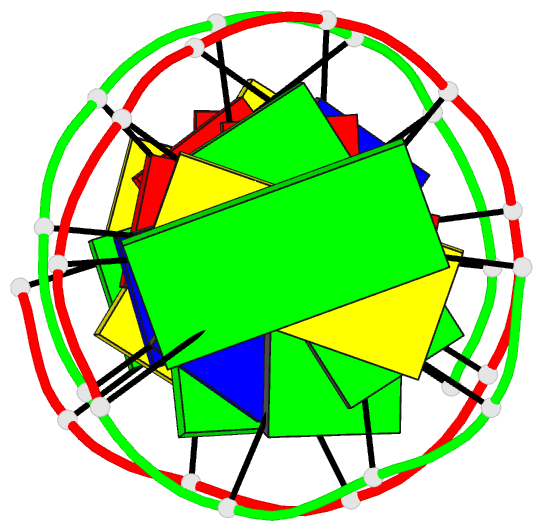
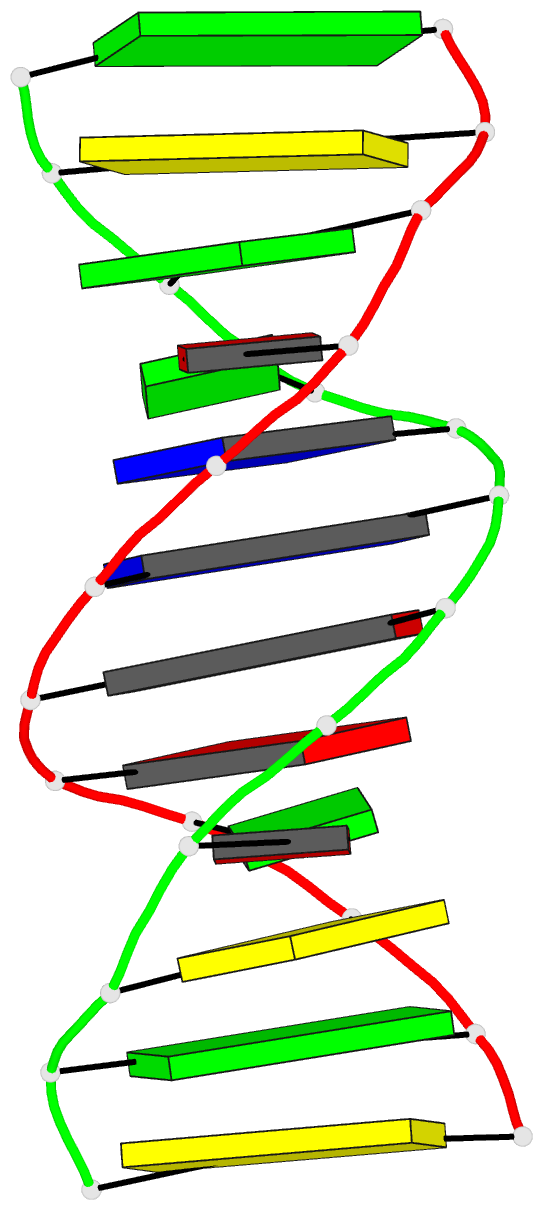
Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
-
150d;
SNAP-derived features in text and
JSON formats
- Class
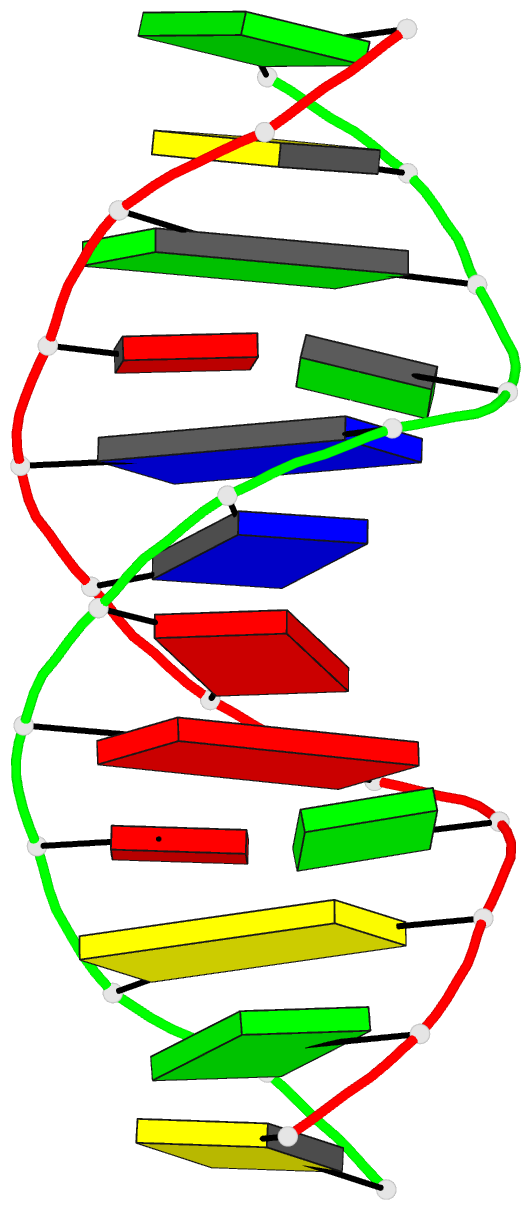
- DNA
- Method
- X-ray (2.25 Å)
- Summary
- Guanine.1,n6-ethenoadenine base-pairs in the crystal
structure of d(cgcgaatt(eda)gcg)
- Reference
-
Leonard GA, McAuley-Hecht KE, Gibson NJ, Brown T, Watson
WP, Hunter WN (1994): "Guanine-1,N6-ethenoadenine
base pairs in the crystal structure of d(CGCGAATT(epsilon
dA)GCG)." Biochemistry, 33,
4755-4761. doi: 10.1021/bi00182a002.
- Abstract
- A single-crystal X-ray analysis of the synthetic
oligomer d(CGCGAATT(epsilon dA)GCG) (epsilon dA =
1,N6-ethenoadenosine) has been carried out. The B-form
duplex crystallizes in the orthorhombic space group
P2(1)2(1)2(1) with unit cell dimensions a = 24.31 A, b =
39.65 A, and c = 63.05 A. Refinement has converged with R =
0.182 for 2837 reflections in the resolution range 7.0-2.25
A for a model consisting of the duplex, one Mg2+ ion, and
127 water molecules. The structure contains two G.epsilon
dA base pairings which adopt a G(anti).epsilon dA(syn)
conformation. The geometry of the two mispairs suggests
that the G.epsilon dA pairing are held together by three
interbase hydrogen bonds. These are N2(G)-H...N1(epsilon
dA), N1(G)...N9(epsilon dA), and O6(G)...H-C8(epsilon dA).
The last interaction serves to alleviate the destabilizing
effect that would occur due to the presence of an
unfulfilled hydrogen bond acceptor. A superposition of the
G(4).epsilon dA-(21) base pair found in this structure and
the Watson-Crick G(4).C(21) base pair observed in the
native dodecamer d(CGCGAATTCGCG) indicates a significant
difference in the sugar/phosphate backbone. However, the
overall conformations of the two duplexes remain similar,
suggesting that the modified base pairs are accommodated
into the double helix mainly by alterations of the backbone
conformation. Such structural rearrangement of the
backbone, upon incorporation of epsilon dA, may provide a
signal to the 3-methyladenine-DNA glycosylase that repairs
such lesions.